Targeted disruption of the mouse transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene results in multifocal inflammatory disease
- PMID: 1436033
- PMCID: PMC3889166
- DOI: 10.1038/359693a0
Targeted disruption of the mouse transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene results in multifocal inflammatory disease
Abstract
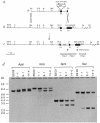
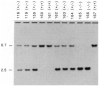
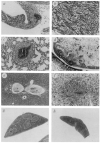
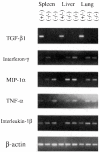
Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) is a multifunctional growth factor that has profound regulatory effects on many developmental and physiological processes. Disruption of the TGF-beta 1 gene by homologous recombination in murine embryonic stem cells enables mice to be generated that carry the disrupted allele. Animals homozygous for the mutated TGF-beta 1 allele show no gross developmental abnormalities, but about 20 days after birth they succumb to a wasting syndrome accompanied by a multifocal, mixed inflammatory cell response and tissue necrosis, leading to organ failure and death. TGF-beta 1-deficient mice may be valuable models for human immune and inflammatory disorders, including autoimmune diseases, transplant rejection and graft versus host reactions.
Figures
References
-
- Barnard JA, Lyons RM, Moses HL. Biochlm biophys.Acta. 1990;1032:79–87. - PubMed
-
- Massague JA. Rev. Cell. Biol. 1990;6:597–641. - PubMed
-
- Roberts AB, Sporn MB. In: Peptide Growth Factors and Their Receptors I. Sporn MB, Roberts AB, editors. Springer; New York: 1990. pp. 419–472.
-
- Lehnert SA, Akhurst RJ. Development. 1988;104:263–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

