Spinal 5-HT(2) and 5-HT(3) receptors mediate low, but not high, frequency TENS-induced antihyperalgesia in rats
- PMID: 14499437
- PMCID: PMC2746627
- DOI: 10.1016/s0304-3959(03)00207-0
Spinal 5-HT(2) and 5-HT(3) receptors mediate low, but not high, frequency TENS-induced antihyperalgesia in rats
Erratum in
- Pain. 2004 Jan;107(1-2):197
Abstract
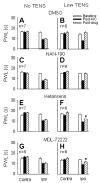
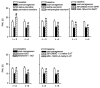
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is a form of non-pharmacological treatment for pain. Involvement of descending inhibitory systems is implicated in TENS-induced analgesia. In the present study, the roles of spinal 5-HT and alpha(2)-adrenoceptors in TENS analgesia were investigated in rats. Hyperalgesia was induced by inflaming the knee joint with 3% kaolin-carrageenan mixture and assessed by measuring paw withdrawal latency (PWL) to heat before and 4 h after injection. The (1). alpha(2)-adrenergic antagonist yohimbine (30 microg), (2). 5-HT antagonist methysergide (5-HT(1). and 5-HT(2). 30 microg), one of the 5-HT receptor subtype antagonists, (3). NAN-190 (5-HT(1A), 15 microg), (4). ketanserin (5-HT(2A), 30 microg), (5). MDL-72222 (5-HT(3), 12 microg), or (6). vehicle was administered intrathecally prior to TENS treatment. Low (4 Hz) or high (100 Hz) frequency TENS at sensory intensity was then applied to the inflamed knee for 20 min and PWL was determined. Selectivity of the antagonists used was confirmed using respective agonists administered intrathecally. Yohimbine had no effect on the antihyperalgesia produced by low or high frequency TENS. Methysergide and MDL-72222 prevented the antihyperalgesia produced by low, but not high, frequency TENS. Ketanserin attenuated the antihyperalgesic effects of low frequency TENS whereas NAN-190 had no effect. The results from the present study show that spinal 5-HT receptors mediate low, but not high, frequency TENS-induced antihyperalgesia through activation of 5-HT(2A) and 5-HT(3) receptors in rats. Furthermore, spinal noradrenergic receptors are not involved in either low or high frequency TENS antihyperalgesia.
Figures

References
-
- Aimone LD, Jones SL, Gebhart GF. Stimulation-produced descending inhibition from the periaqueductal gray and nucleus raphe magnus in the rat: mediation by spinal monoamines but not opioids. Pain. 1987;31:123–36. - PubMed
-
- Alhaider AA, Wilcox GL. Differential roles of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A and 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptor subtypes in modulating spinal nociceptive transmission in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;265:378–85. - PubMed
-
- Almay BG, Johansson F, von Knorring L, Sakurada T, Terenius L. Long-term high frequency transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (hi-TNS) in chronic pain. Clinical response and effects on CSF-endorphins, monoamine metabolites, substance P-like immunoreactivity (SPLI) and pain measures. J Psychosom Res. 1985;29:247–57. - PubMed
-
- Aran S, Proudfit HK. Antinociception produced by interactions between intrathecally administered adenosine agonists and norepinephrine. Brain Res. 1990;513:255–63. - PubMed
-
- Bardin L, Bardin M, Lavarenne J, Eschalier A. Effect of intrathecal serotonin on nociception in rats: influence of the pain test used. Exp Brain Res. 1997;113:81–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

