Identification and characterization of a new staphylococcal enterotoxin-related putative toxin encoded by two kinds of plasmids
- PMID: 14500536
- PMCID: PMC201035
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.10.6088-6094.2003
Identification and characterization of a new staphylococcal enterotoxin-related putative toxin encoded by two kinds of plasmids
Abstract
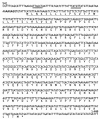
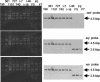
We identified and characterized a novel staphylococcal enterotoxin-like putative toxin, which is named SER. Nucleotide sequencing analysis of the ser gene revealed that ser was most closely related to the seg gene. The ser gene product, SER, was successfully expressed as a recombinant protein in an Escherichia coli expression system, and recombinant SER (rSER) showed significant T-cell stimulation activity. The SER production in ser-harboring Staphylococcus aureus strains was confirmed by Western blot analysis using anti-rSER antibody. Moreover, ser was seen to be encoded by at least two types of plasmids. In particular, one kind of plasmid encoding the ser gene has been known as a sed- and sej-carrying pIB485-related plasmid.
Figures

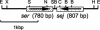


Similar articles
-
Detection of the staphylococcal enterotoxin D-like gene from staphylococcal food poisoning isolates over the last two decades in Tokyo.J Vet Med Sci. 2015 Aug;77(8):905-11. doi: 10.1292/jvms.15-0028. Epub 2015 Mar 20. J Vet Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25797800 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of staphylococcal enterotoxin types G and I from Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Immun. 1998 Jul;66(7):3337-48. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.7.3337-3348.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9632603 Free PMC article.
-
Enterotoxins and toxic shock syndrome toxin in Staphylococcus aureus recovered from human nasal carriers and manually handled foods: epidemiological and genetic findings.Microbes Infect. 2005 Feb;7(2):187-94. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2004.10.009. Epub 2005 Jan 5. Microbes Infect. 2005. PMID: 15715991
-
Sequence Variability in Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Genes seb, sec, and sed.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Jun 1;8(6):169. doi: 10.3390/toxins8060169. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27258311 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcal enterotoxins.Int J Food Microbiol. 2000 Oct 1;61(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1605(00)00377-9. Int J Food Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11028954 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in organic milk and cheese in Tabriz, Iran.Iran J Microbiol. 2014 Oct;6(5):345-9. Iran J Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25848526 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the Enterotoxigenic Potential of Staphylococcus spp. from Raw Milk and Raw Milk Cheeses.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Dec 28;16(1):17. doi: 10.3390/toxins16010017. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38251234 Free PMC article.
-
Major families of multiresistant plasmids from geographically and epidemiologically diverse staphylococci.G3 (Bethesda). 2011 Dec;1(7):581-91. doi: 10.1534/g3.111.000760. Epub 2011 Dec 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2011. PMID: 22384369 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of novel staphylococcal enterotoxin-like toxin type P.Infect Immun. 2005 Sep;73(9):5540-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.9.5540-5546.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16113270 Free PMC article.
-
Accessory gene regulator control of staphyloccoccal enterotoxin d gene expression.J Bacteriol. 2004 Mar;186(6):1793-801. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.6.1793-1801.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 14996810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arcus, V. L., R. Langley, T. Proft, J. D. Fraser, and E. N. Baker. 2002. The three-dimensional structure of a superantigen-like protein, SET3, from a pathogenicity island of the Staphylococcus aureus genome. J. Biol. Chem. 277:32274-32281. - PubMed
-
- Baba, T., F. Takeuchi, M. Kuroda, H. Yuzawa, K. Aoki, A. Oguchi, Y. Nagai, N. Iwama, K. Asano, T. Naimi, H. Kuroda, L. Cui, K. Yamamoto, and K. Hiramatsu. 2002. Genome and virulence determinants of high virulence community-acquired MRSA. Lancet 359:1819-1827. - PubMed
-
- Bergdoll, M. S. 1988. Monkey feeding test for staphylococcal enterotoxin. Methods Enzymol. 165:324-333. - PubMed
-
- Bergdoll, M. S. 1989. Staphylococcus aureus, p. 463-523. In M. P. Doyle (ed.), Foodborne bacterial pathogens. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

