Variable amplification of synaptic input to cat spinal motoneurones by dendritic persistent inward current
- PMID: 14500771
- PMCID: PMC2343455
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.050971
Variable amplification of synaptic input to cat spinal motoneurones by dendritic persistent inward current
Abstract
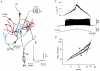
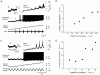
Electrophysiological and computational evidence indicate that the excitatory current from the synapses on the somato-dendritic membrane is not large enough to drive the motoneurones to the firing frequencies actually attained under normal motor activity. It has been proposed that this paradox could be explained if the voltage-dependent persistent inward currents (PICs) present in the dendrites of motoneurones served to amplify synaptic excitation. We report here that dendritic PICs cause a large amplification of synaptic excitation, and that this amplification is enhanced when the background firing by current injection is increased. Moreover the frequency reduction by synaptic inhibition is greatly enhanced at higher firing frequencies, when the current through the recording electrode has activated the dendritic PICs, as is the case when the current-to-frequency slope suddenly becomes steeper. We also demonstrate that synaptic inhibition is several times more effective in reducing the firing caused by synaptic excitation than firing evoked by current injection through the recording microelectrode. That would be explained if motoneuronal discharge by synaptic excitation--but not by current injection in the soma--is always supported by dendritic PICs. We conclude that dendritic PICs contribute dynamically to the transformation of synaptic input into a motoneuronal frequency code.
Figures

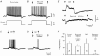
Comment in
-
Intrinsic dendritic currents make a major contribution to the control of motoneurone discharge.J Physiol. 2003 Nov 1;552(Pt 3):665. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.054817. Epub 2003 Sep 26. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 14514880 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bennett DJ, Hultborn H, Fedirchuk B, Gorassini M. Synaptic activation of plateaus in hindlimb motoneurons of decerebrate cats. J Neurophysiol. 1998;80:2023–2037. - PubMed
-
- Binder MD. Integration of synaptic and intrinsic dendritic currents in cat spinal motoneurons. Brain Res Rev. 2003;40:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Carlin KP, Jones KE, Jiang Z, Jordan LM, Brownstone RM. Dendritic L-type calcium currents in mouse spinal motoneurons: implications for bistability. Eur J Neurosc. 2000;12:1635–1646. - PubMed
-
- Fyffe RE. Spatial distribution of recurrent inhibitory synapses on spinal motoneurons in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1991;65:1134–1149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

