An essential function of the mitogen-activated protein kinase Erk2 in mouse trophoblast development
- PMID: 14502223
- PMCID: PMC1326397
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor939
An essential function of the mitogen-activated protein kinase Erk2 in mouse trophoblast development
Abstract
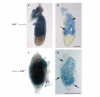
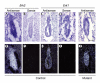
The closely related mitogen-activated protein kinase isoforms extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) and ERK2 have been implicated in the control of cell proliferation, differentiation and survival. However, the specific in vivo functions of the two ERK isoforms remain to be analysed. Here, we show that disruption of the Erk2 locus leads to embryonic lethality early in mouse development after the implantation stage. Erk2 mutant embryos fail to form the ectoplacental cone and extra-embryonic ectoderm, which give rise to mature trophoblast derivatives in the fetus. Analysis of chimeric embryos showed that Erk2 functions in a cell-autonomous manner during the development of extra-embryonic cell lineages. We also found that both Erk2 and Erk1 are widely expressed throughout early-stage embryos. The inability of Erk1 to compensate for Erk2 function suggests a specific function for Erk2 in normal trophoblast development in the mouse, probably in regulating the proliferation of polar trophectoderm cells.
Figures
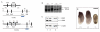

References
-
- Ang S.L, Conlon R.A., Jin O. & Rossant J. ( 1994) Positive and negative signals from mesoderm regulate the expression of mouse Otx2 in ectoderm explants. Development, 120, 2979–2989. - PubMed
-
- Ballif B.A. & Blenis J. ( 2001) Molecular mechanisms mediating mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MEK)–MAPK cell survival signals. Cell Growth Differ., 12, 397–408. - PubMed
-
- Beddington R.S. & Robertson E.J. ( 1989) An assessment of the developmental potential of embryonic stem cells in the midgestation mouse embryo. Development, 105, 733–737. - PubMed
-
- Boulton T.G. et al. . ( 1990) An insulin-stimulated protein kinase similar to yeast kinases involved in cell cycle control. Science, 249, 64–67. - PubMed
-
- Boulton T.G. et al. . ( 1991) ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell, 65, 663–675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

