Comparative inhibition by substrate analogues 3-methoxy- and 3-hydroxydesaminokynurenine and an improved 3 step purification of recombinant human kynureninase
- PMID: 14505498
- PMCID: PMC223355
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2091-4-13
Comparative inhibition by substrate analogues 3-methoxy- and 3-hydroxydesaminokynurenine and an improved 3 step purification of recombinant human kynureninase
Abstract
Background: Kynureninase is a key enzyme on the kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism. One of the end products of the pathway is the neurotoxin quinolinic acid which appears to be responsible for neuronal cell death in a number of important neurological diseases. This makes kynureninase a possible therapeutic target for diseases such as Huntington's, Alzheimer's and AIDS related dementia, and the development of potent inhibitors an important research aim.
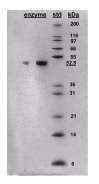
Results: Two new kynurenine analogues, 3-hydroxydesaminokynurenine and 3-methoxydesaminokynurenine, were synthesised as inhibitors of kynureninase and tested on the tryptophan-induced bacterial enzyme from Pseudomonas fluorescens, the recombinant human enzyme and the rat hepatic enzyme. They were found to be mixed inhibitors of all three enzymes displaying both competitive and non competitive inhibition. The 3-hydroxy derivative gave low Ki values of 5, 40 and 100 nM respectively. An improved 3-step purification scheme for recombinant human kynureninase was also developed.
Conclusion: For kynureninase from all three species the 2-amino group was found to be crucial for activity whilst the 3-hydroxyl group played a fundamental role in binding at the active site presumably via hydrogen bonding. The potency of the various inhibitors was found to be species specific. The 3-hydroxylated inhibitor had a greater affinity for the human enzyme, consistent with its specificity for 3-hydroxykynurenine as substrate, whilst the methoxylated version yielded no significant difference between bacterial and human kynureninase. The modified purification described is relatively quick, simple and cost effective.
Figures
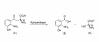



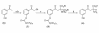
Similar articles
-
A comparative study on the inhibition of human and bacterial kynureninase by novel bicyclic kynurenine analogues.Bioorg Med Chem. 2001 Apr;9(4):983-9. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(00)00318-7. Bioorg Med Chem. 2001. PMID: 11354681
-
Differential effects of bromination on substrates and inhibitors of kynureninase from Pseudomonas fluorescens.Org Biomol Chem. 2003 Jan 21;1(2):288-95. doi: 10.1039/b208910f. Org Biomol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12929424
-
Crystal structure of the Homo sapiens kynureninase-3-hydroxyhippuric acid inhibitor complex: insights into the molecular basis of kynureninase substrate specificity.J Med Chem. 2009 Jan 22;52(2):389-96. doi: 10.1021/jm8010806. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19143568
-
Structure and mechanism of kynureninase.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014 Feb 15;544:69-74. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2013.10.020. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014. PMID: 24200862 Review.
-
Kynurenine hydroxylase and kynureninase inhibitors as tools to study the role of kynurenine metabolites in the central nervous system.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1996;398:203-10. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-0381-7_33. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1996. PMID: 8906267 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism: Regulatory and Functional Aspects.Int J Tryptophan Res. 2017 Mar 15;10:1178646917691938. doi: 10.1177/1178646917691938. eCollection 2017. Int J Tryptophan Res. 2017. PMID: 28469468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterisation of the organophosphate hydrolase catalytic activity of SsoPox.Sci Rep. 2012;2:779. doi: 10.1038/srep00779. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Sci Rep. 2012. PMID: 23139857 Free PMC article.
-
Kynurenines in the CNS: recent advances and new questions.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Jan;12(1):64-82. doi: 10.1038/nrd3793. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23237916 Review.
-
Kynurenines with neuroactive and redox properties: relevance to aging and brain diseases.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:646909. doi: 10.1155/2014/646909. Epub 2014 Feb 17. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014. PMID: 24693337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kynurenines and Glutamate: Multiple Links and Therapeutic Implications.Adv Pharmacol. 2016;76:13-37. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2016.01.005. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Adv Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27288072 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Botting NP. Chemistry and Neurochemistry of the Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism. Chem Soc Rev. 1993;45:309–315.
-
- Nishizuka Y, Hayaishi O. Studies on the biosynthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. J Biochem. 1963;238:3368–3377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

