Genetic analysis of the influence of neuroantigen-complete Freund's adjuvant emulsion structures on the sexual dimorphism and susceptibility to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 14507669
- PMCID: PMC1868279
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63519-5
Genetic analysis of the influence of neuroantigen-complete Freund's adjuvant emulsion structures on the sexual dimorphism and susceptibility to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis
Abstract
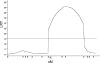
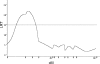
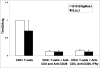
The induction of organ-specific autoimmune diseases, such as experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) the principal animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS), relies on the use of complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) emulsions. In this study we report that the physical structure of the particles comprising neuroantigen-CFA emulsions significantly influences the genetic control of the incidence and sexual dimorphism seen in EAE. Immunization of (B10.S/SgMcdJ x SJL/J) F(2) mice segregating the quantitative trait loci (QTL) controlling EAE in susceptible SJL/J and resistant B10.S/SgMcdJ mice with emulsions consisting of particles where the Mycobacterium tuberculosis and neuroantigens are localized on the phase surfaces led to severe EAE in 98.8% of the mice, overriding all sex-specific and non-sex-specific genetic checkpoints. In contrast, F(2) mice immunized with emulsions where the bacterial products and encephalitogens are buried inside the water/oil vesicles exhibited a significant reduction in disease incidence (7.5%) and a sexual dimorphism (5% male versus 10% female). A genome scan identified QTL on chromosomes 7 and 11 controlling the sexual dimorphism as a function of the physical structure of the emulsion. The chromosome 11 QTL co-localizes with eae6b, and with Il12b and heptatitis A virus cellular receptor 2 (Havcr2, formerly known as Timd3), both of which are candidate genes for this QTL. Sequence analysis of the SJL/J and B10.S/SgMcdJ alleles indicates that both gene products are structurally monomorphic. Expression analysis also excluded both as candidates for this sex-specific QTL. These results reinforce the importance of gene-environment interactions in initiating and propagating autoimmune disease of the central nervous system, particularly in the context of susceptibility to MS and disease heterogeneity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
T cell-depleted splenocytes from mice pre-immunized with neuroantigen in incomplete Freund's adjuvant involved in protection from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Immunol Lett. 2014 Jan-Feb;157(1-2):38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Immunol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24220208
-
Sequence polymorphisms in the chemokines Scya1 (TCA-3), Scya2 (monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1), and Scya12 (MCP-5) are candidates for eae7, a locus controlling susceptibility to monophasic remitting/nonrelapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis.J Immunol. 1999 Aug 15;163(4):2262-6. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10438970
-
Identification of genetic loci controlling the characteristics and severity of brain and spinal cord lesions in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis.Am J Pathol. 2000 Aug;157(2):637-45. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64574-9. Am J Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10934166 Free PMC article.
-
AN ANALYSIS OF COMPONENTS OF FREUND'S ADJUVANTS IN THE PRODUCTION OF EXPERIMENTAL "ALLERGIC" ENCEPHALOMYELITIS IN THE GUINEA PIG.Z Immunitats Allergieforsch. 1964 Mar;126:193-208. Z Immunitats Allergieforsch. 1964. PMID: 14185397 Review. No abstract available.
-
Complete Freund's adjuvant as a confounding factor in multiple sclerosis research.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 15;15:1353865. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1353865. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38426111 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
eae36, a locus on mouse chromosome 4, controls susceptibility to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in older mice and mice immunized in the winter.Genetics. 2006 Feb;172(2):1147-53. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.049049. Epub 2005 Nov 19. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16299394 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple linked quantitative trait loci within the Tmevd2/Eae3 interval control the severity of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in DBA/2J mice.Genes Immun. 2010 Dec;11(8):649-59. doi: 10.1038/gene.2010.40. Epub 2010 Sep 23. Genes Immun. 2010. PMID: 20861860 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling multiple sclerosis in laboratory animals.Semin Immunopathol. 2009 Nov;31(4):479-95. doi: 10.1007/s00281-009-0181-4. Epub 2009 Oct 3. Semin Immunopathol. 2009. PMID: 19802608 Review.
-
Chemokines Referee Inflammation within the Central Nervous System during Infection and Disease.Adv Med. 2014;2014:806741. doi: 10.1155/2014/806741. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Adv Med. 2014. PMID: 26556427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutting edge: the Y chromosome controls the age-dependent experimental allergic encephalomyelitis sexual dimorphism in SJL/J mice.J Immunol. 2009 Feb 15;182(4):1789-93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803200. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19201829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Freund J, Stern ER, Pisami TM: Isoallergic encephalomyelitis and radiculitis in guinea pigs after one injection of brain and mycobacteria in water-in-oil emulsion. J Immunol 1947, 57:179-194 - PubMed
-
- Billiau A, Matthys P: Modes of action of Freund’s adjuvants in experimental models of autoimmune diseases. J Leuk Biol 2001, 70:849-860 - PubMed
-
- Mancini RE, Andrada JA, Saraceni A, Bachmann AE, Lavieri JC, Nemirovsky M: Immunological and testicular response in man sensitized with human testicular homogenate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1965, 25:859-875 - PubMed
-
- Drachman DA, Paterson PY, Bornstein MB: Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in man: a laboratory accident. Neurology 1974, 24:364
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

