Proteasome inhibitor (MG-132) treatment of mdx mice rescues the expression and membrane localization of dystrophin and dystrophin-associated proteins
- PMID: 14507673
- PMCID: PMC1868305
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63523-7
Proteasome inhibitor (MG-132) treatment of mdx mice rescues the expression and membrane localization of dystrophin and dystrophin-associated proteins
Abstract
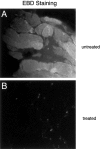
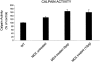
Dystrophin, the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene, is absent in the skeletal muscle of DMD patients and mdx mice. At the plasma membrane of skeletal muscle fibers, dystrophin associates with a multimeric protein complex, termed the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC). Protein members of this complex are normally absent or greatly reduced in dystrophin-deficient skeletal muscle fibers, and are thought to undergo degradation through an unknown pathway. As such, we reasoned that inhibition of the proteasomal degradation pathway might rescue the expression and subcellular localization of dystrophin-associated proteins. To test this hypothesis, we treated mdx mice with the well-characterized proteasomal inhibitor MG-132. First, we locally injected MG-132 into the gastrocnemius muscle, and observed the outcome after 24 hours. Next, we performed systemic treatment using an osmotic pump that allowed us to deliver different concentrations of the proteasomal inhibitor, over an 8-day period. By immunofluorescence and Western blot analysis, we show that administration of the proteasomal inhibitor MG-132 effectively rescues the expression levels and plasma membrane localization of dystrophin, beta-dystroglycan, alpha-dystroglycan, and alpha-sarcoglycan in skeletal muscle fibers from mdx mice. Furthermore, we show that systemic treatment with the proteasomal inhibitor 1) reduces muscle membrane damage, as revealed by vital staining (with Evans blue dye) of the diaphragm and gastrocnemius muscle isolated from treated mdx mice, and 2) ameliorates the histopathological signs of muscular dystrophy, as judged by hematoxylin and eosin staining of muscle biopsies taken from treated mdx mice. Thus, the current study opens new and important avenues in our understanding of the pathogenesis of DMD. Most importantly, these new findings may have clinical implications for the pharmacological treatment of patients with DMD.
Figures






References
-
- Hoffman EP, Brown RH, Kunkel LM: Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell 1987, 51:919-928 - PubMed
-
- Ervasti JM, Campbell KP: Membrane organization of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex. Cell 1991, 66:1121-1131 - PubMed
-
- Brenman JE, Chao DS, Xia H, Aldape K, Bredt DS: Nitric oxide synthase complexed with dystrophin and absent from skeletal muscle sarcolemma in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Cell 1995, 82:743-752 - PubMed
-
- Crosbie RH, Yamada H, Venzke DP, Lisanti MP, Campbell KP: Caveolin-3 is not an essential component of the dystrophin glycoprotein complex. FEBS Lett 1998, 427:279-282 - PubMed
-
- Song KS, Scherer PE, Tang Z-L, Okamoto T, Li S, Chafel M, Chu C, Kohtz DS, Lisanti MP: Expression of caveolin-3 in skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle cells: caveolin-3 is a component of the sarcolemma and co-fractionates with dystrophin and dystrophin-associated glycoproteins. J Biol Chem 1996, 271:15160-15165 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

