Biosilica formation in diatoms: characterization of native silaffin-2 and its role in silica morphogenesis
- PMID: 14507995
- PMCID: PMC218715
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2035131100
Biosilica formation in diatoms: characterization of native silaffin-2 and its role in silica morphogenesis
Abstract
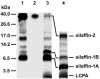
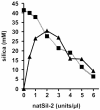
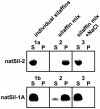
The biological formation of inorganic materials with complex form (biominerals) is a widespread phenomenon in nature, yet the molecular mechanisms underlying biomineral morphogenesis are not well understood. Among the most fascinating examples of biomineral structures are the intricately patterned, silicified cell walls of diatoms, which contain tightly associated organic macromolecules. From diatom biosilica a highly polyanionic phosphoprotein, termed native silaffin-2 (natSil-2), was isolated that carries unconventional amino acid modifications. natSil-2 lacked intrinsic silica formation activity but was able to regulate the activities of the previously characterized silica-forming biomolecules natSil-1A and long-chain polyamines. Combining natSil-2 and natSil-1A (or long-chain polyamines) generated an organic matrix that mediated precipitation of porous silica within minutes after the addition of silicic acid. Remarkably, the precipitate displayed pore sizes in the range 100-1000 nm, which is characteristic for diatom biosilica nanopatterns.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nanopatterned protein microrings from a diatom that direct silica morphogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 22;108(8):3175-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1012842108. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21300899 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembly of highly phosphorylated silaffins and their function in biosilica morphogenesis.Science. 2002 Oct 18;298(5593):584-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1076221. Science. 2002. PMID: 12386330
-
Reconstituting the formation of hierarchically porous silica patterns using diatom biomolecules.J Struct Biol. 2018 Oct;204(1):64-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2018.07.005. Epub 2018 Jul 29. J Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 30009877
-
Diatoms-from cell wall biogenesis to nanotechnology.Annu Rev Genet. 2008;42:83-107. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.41.110306.130109. Annu Rev Genet. 2008. PMID: 18983255 Review.
-
Preparation of biosilica structures from frustules of diatoms and their applications: current state and perspectives.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Jan;97(2):453-60. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4568-0. Epub 2012 Nov 18. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23179621 Review.
Cited by
-
Formation of asymmetrical structured silica controlled by a phase separation process and implication for biosilicification.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 9;8(4):e61164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061164. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23585878 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of an endoplasmic reticulum-associated silaffin kinase from the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 8;285(2):1166-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.039529. Epub 2009 Nov 4. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19889629 Free PMC article.
-
Biomedical applications of solid-binding peptides and proteins.Mater Today Bio. 2023 Feb 15;19:100580. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100580. eCollection 2023 Apr. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 36846310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From biosilicification to tailored materials: optimizing hydrophobic domains and resistance to protonation of polyamines.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 22;105(16):5963-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710809105. Epub 2008 Apr 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18420819 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of Bacterial Contamination of a Silica Matrix Containing Entrapped β-Galactosidase through the Action of Covalently Bound Lysozymes.Molecules. 2017 Feb 28;22(3):377. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030377. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28264511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lowenstam, H. A. & Weiner, S. (1989) On Biomineralization (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford).
-
- Perry, C. C. & Keeling-Tucker, T. (2000) J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 5, 537–550. - PubMed
-
- Bäuerlein, E. (2000) Biomineralization (Wiley–VCH, Weinheim, Germany).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

