Arabidopsis sfd mutants affect plastidic lipid composition and suppress dwarfing, cell death, and the enhanced disease resistance phenotypes resulting from the deficiency of a fatty acid desaturase
- PMID: 14507997
- PMCID: PMC197303
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.015529
Arabidopsis sfd mutants affect plastidic lipid composition and suppress dwarfing, cell death, and the enhanced disease resistance phenotypes resulting from the deficiency of a fatty acid desaturase
Abstract
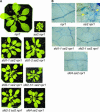
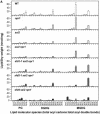
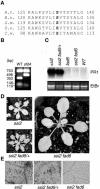
A loss-of-function mutation in the Arabidopsis SSI2/FAB2 gene, which encodes a plastidic stearoyl-acyl-carrier protein desaturase, has pleiotropic effects. The ssi2 mutant plant is dwarf, spontaneously develops lesions containing dead cells, accumulates increased salicylic acid (SA) levels, and constitutively expresses SA-mediated, NPR1-dependent and -independent defense responses. In parallel, jasmonic acid-regulated signaling is compromised in the ssi2 mutant. In an effort to discern the involvement of lipids in the ssi2-conferred developmental and defense phenotypes, we identified suppressors of fatty acid (stearoyl) desaturase deficiency (sfd) mutants. The sfd1, sfd2, and sfd4 mutant alleles suppress the ssi2-conferred dwarfing and lesion development, the NPR1-independent expression of the PATHOGENESIS-RELATED1 (PR1) gene, and resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv maculicola. The sfd1 and sfd4 mutant alleles also depress ssi2-conferred PR1 expression in NPR1-containing sfd1 ssi2 and sfd4 ssi2 plants. By contrast, the sfd2 ssi2 plant retains the ssi2-conferred high-level expression of PR1. In parallel with the loss of ssi2-conferred constitutive SA signaling, the ability of jasmonic acid to activate PDF1.2 expression is reinstated in the sfd1 ssi2 npr1 plant. sfd4 is a mutation in the FAD6 gene that encodes a plastidic omega6-desaturase that is involved in the synthesis of polyunsaturated fatty acid-containing lipids. Because the levels of plastid complex lipid species containing hexadecatrienoic acid are depressed in all of the sfd ssi2 npr1 plants, we propose that these lipids are involved in the manifestation of the ssi2-conferred phenotypes.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Plastidial fatty acid signaling modulates salicylic acid- and jasmonic acid-mediated defense pathways in the Arabidopsis ssi2 mutant.Plant Cell. 2003 Dec;15(12):2952-65. doi: 10.1105/tpc.017301. Epub 2003 Nov 13. Plant Cell. 2003. PMID: 14615603 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced resistance to Cucumber mosaic virus in the Arabidopsis thaliana ssi2 mutant is mediated via an SA-independent mechanism.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004 Jun;17(6):623-32. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.6.623. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004. PMID: 15195945
-
Restoration of defective cross talk in ssi2 mutants: role of salicylic acid, jasmonic acid, and fatty acids in SSI2-mediated signaling.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003 Nov;16(11):1022-9. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2003.16.11.1022. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003. PMID: 14601670
-
Arabidopsis ssi2-conferred susceptibility to Botrytis cinerea is dependent on EDS5 and PAD4.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2005 Apr;18(4):363-70. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-18-0363. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2005. PMID: 15828688
-
The Arabidopsis thaliana dihydroxyacetone phosphate reductase gene SUPPRESSSOR OF FATTY ACID DESATURASE DEFICIENCY1 is required for glycerolipid metabolism and for the activation of systemic acquired resistance.Plant Cell. 2004 Feb;16(2):465-77. doi: 10.1105/tpc.016907. Epub 2004 Jan 16. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 14729910 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry is a powerful tool to study glycerolipid composition in plants with different level of desaturase activity.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 May;8(5):e24118. doi: 10.4161/psb.24118. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23470727 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of plant defense responses in Arabidopsis by EDR2, a PH and START domain-containing protein.Plant J. 2005 Oct;44(2):245-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02523.x. Plant J. 2005. PMID: 16212604 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic responses to the reduction in palmitate caused by disruption of the FATB gene in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2004 Jul;135(3):1269-79. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.043372. Plant Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15266055 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidomic Analysis of Arabidopsis T-DNA Insertion Lines Leads to Identification and Characterization of C-Terminal Alterations in FATTY ACID DESATURASE 6.Plant Cell Physiol. 2022 Sep 15;63(9):1193-1204. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcac088. Plant Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35726963 Free PMC article.
-
Transplastomic tobacco plants expressing a fatty acid desaturase gene exhibit altered fatty acid profiles and improved cold tolerance.Transgenic Res. 2008 Oct;17(5):769-82. doi: 10.1007/s11248-008-9164-9. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Transgenic Res. 2008. PMID: 18214708
References
-
- Anderson, M.D., Chen, Z., and Klessig, D.F. (1998). Possible involvement of lipid peroxidation in salicylic acid-mediated induction of PR1 gene expression. Phytochemistry 47, 555–566.
-
- Bell, C.J., and Ecker, J.R. (1994). Assignment of 30 microsatellite loci to the linkage map of Arabidopsis. Genomics 19, 137–144. - PubMed
-
- Berrocal-Lobo, M., Molina, A., and Solano, R. (2002). Constitutive expression of ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR1 in Arabidopsis confers resistance to several necrotrophic fungi. Plant J. 29, 23–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

