HLA-DRB1*1101: a significant risk factor for sarcoidosis in blacks and whites
- PMID: 14508706
- PMCID: PMC1180597
- DOI: 10.1086/378097
HLA-DRB1*1101: a significant risk factor for sarcoidosis in blacks and whites
Abstract
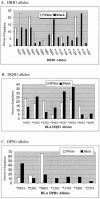
Sarcoidosis is a granulomatous disorder of unknown etiology, associated with an accumulation of CD4+ T cells and a TH1 immune response. Since previous studies of HLA associations with sarcoidosis were limited by serologic or low-resolution molecular identification, we performed high-resolution typing for the HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRB1, and HLA-DRB3 loci and the presence of the DRB4 or DRB5 locus, to define HLA class II associations with sarcoidosis. A Case Control Etiologic Study of Sarcoidosis (ACCESS) enrolled biopsy-confirmed cases (736 total) from 10 centers in the United States. Seven hundred six (706) controls were case matched for age, race, sex, and geographic area. We studied the first 474 ACCESS patients and case-matched controls. The HLA-DRB1 alleles were differentially distributed between cases and controls (P<.0001). The HLA-DRB1*1101 allele was associated (P<.01) with sarcoidosis in blacks and whites and had a population attributable risk of 16% in blacks and 9% in whites. HLA-DRB1-F(47) was the amino acid residue most associated with sarcoidosis and independently associated with sarcoidosis in whites. The HLA-DPB1 locus also contributed to susceptibility for sarcoidosis and, in contrast to chronic beryllium disease, a non-E(69)-containing allele, HLA-DPB1*0101, conveyed most of the risk. Although significant differences were observed in the distribution of HLA class II alleles between blacks and whites, only HLA-DRB1*1501 was differentially associated with sarcoidosis (P<.003). In addition to being susceptibility markers, HLA class II alleles may be markers for different phenotypes of sarcoidosis (DRB1*0401 for eye in blacks and whites, DRB3 for bone marrow in blacks, and DPB1*0101 for hypercalcemia in whites). These studies confirm a genetic predisposition for sarcoidosis and present evidence for the allelic variation at the HLA-DRB1 locus as a major contributor.
Figures
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/
References
-
- Androulakis IP, Nayak NN, Ierapetritou MG, Monos DS, Floudas CA (1997) A predictive method of the evaluation of peptide binding in pocket 1 of HLA-DRB1 via global minimization of energy interactions. Proteins Struct Funct Genet 29:87–102 - PubMed
-
- Arbustini E, Grasso M, Leo G, Tinelli C, Fasani R, Diegoli M, Banchieri N, Cipriani A, Gorrini M, Semenzato G, Luisetti M (1996) Polymorphisms of angiotensin-converting enzyme gene in sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 153:851–854 - PubMed
-
- Baughman R, Teirstein A, Judson M, Rossman MD, Yeager HJ, Bresnitz EA, DePalo L, Hunninghake G, Iannuzzi MC, Johns CJ, McLennan G, Moller DR, Newman LS, Rabin DL, Rose C, Rybicki B, Weinberger SE, Terrin ML, Knatterud GL, Cherniak R (2001) Clinical characteristics of patietns in a case control etiology study of sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1885–1889 - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner KB, Samet JM, Coultas DB, Stidley CA, Hunt WC, Colby TV, Waldron JA (2000) Occupational and environmental risk factors for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a multicenter case-control study. Am J Epidemiol 152:307–315 - PubMed
-
- Begovich AB, McClure GR, Suraj VC, Helmuth RC, Fildes N, Bugawan TL, Erlich HA, Klitz W (1992) Polymorphism, recombination, and linkage disequilibrium within the HLA class II region. J Immunol 148:249–258 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-HR-56073/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-56068/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-56074/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-56066/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-56069/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-56065/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR056075/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-56072/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-56070/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-56075/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-56067/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007785/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-56071/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

