Identification of four highly conserved genes between breakpoint hotspots BP1 and BP2 of the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndromes deletion region that have undergone evolutionary transposition mediated by flanking duplicons
- PMID: 14508708
- PMCID: PMC1180611
- DOI: 10.1086/378816
Identification of four highly conserved genes between breakpoint hotspots BP1 and BP2 of the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndromes deletion region that have undergone evolutionary transposition mediated by flanking duplicons
Abstract
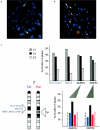
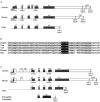
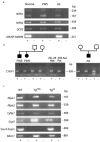
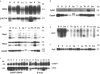
Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes (PWS and AS) typically result from an approximately 4-Mb deletion of human chromosome 15q11-q13, with clustered breakpoints (BP) at either of two proximal sites (BP1 and BP2) and one distal site (BP3). HERC2 and other duplicons map to these BP regions, with the 2-Mb PWS/AS imprinted domain just distal of BP2. Previously, the presence of genes and their imprinted status have not been examined between BP1 and BP2. Here, we identify two known (CYFIP1 and GCP5) and two novel (NIPA1 and NIPA2) genes in this region in human and their orthologs in mouse chromosome 7C. These genes are expressed from a broad range of tissues and are nonimprinted, as they are expressed in cells derived from normal individuals, patients with PWS or AS, and the corresponding mouse models. However, replication-timing studies in the mouse reveal that they are located in a genomic domain showing asynchronous replication, a feature typically ascribed to monoallelically expressed loci. The novel genes NIPA1 and NIPA2 each encode putative polypeptides with nine transmembrane domains, suggesting function as receptors or as transporters. Phylogenetic analyses show that NIPA1 and NIPA2 are highly conserved in vertebrate species, with ancestral members in invertebrates and plants. Intriguingly, evolutionary studies show conservation of the four-gene cassette between BP1 and BP2 in human, including NIPA1/2, CYFIP1, and GCP5, and proximity to the Herc2 gene in both mouse and Fugu. These observations support a model in which duplications of the HERC2 gene at BP3 in primates first flanked the four-gene cassette, with subsequent transposition of these four unique genes by a HERC2 duplicon-mediated process to form the BP1-BP2 region. Duplicons therefore appear to mediate genomic fluidity in both disease and evolutionary processes.
Figures






References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Biological Software, Institut Pasteur, http://bioweb.pasteur.fr/intro-uk.html (for the CLUSTAL W identity/similarity matrix program and the drawtree program to plot unrooted tree diagrams)
-
- Fugu BLAST Server, http://fugu.hgmp.mrc.ac.uk/blast/blast.cgi (for BLAST searches to identify the Fugu p, Herc2, Nipa1, Nipa2, Cyfip1, and Gcp5 gene orthologs)
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for mouse Nipa1 cDNA [accession number AY098645], for chicken Nipa2 cDNA [accession number AY099502], for human NIPA1 cDNA [accession number BK001020], for human NIPA2 cDNA [accession number BK001120], for mouse Nipa2 cDNA [accession number BK001121], and for Xenopus Nipa2 cDNA [accession number BK001125])
-
- GeneMap '98, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genemap98/
-
- NCBI BLAST, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/ (for BLAST searches)
References
-
- Amos-Landgraf JM, Ji Y, Wayne G, Depinet T, Wandstrat SB, Daniel JD, Rogan PK, Schwartz S, Nicholls RD (1999) Chromosome breakage in the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes involves recombination between large, transcribed repeats at proximal and distal breakpoints. Am J Hum Genet 65:370–386 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boccaccio I, Glatt-Deeley H, Watrin F, Roëckel N, Lalande M, Muscatelli F (1999) The human MAGEL2 gene and its mouse homologue are paternally expressed and mapped to the Prader-Willi region. Hum Mol Genet 8:2497–2505 - PubMed
-
- Buiting K, Korner C, Ulrich B, Wahle E, Horsthemke B (1999) The human gene for the poly(A)-specific ribonuclease (PARN) maps to 16p13 and has a truncated copy in the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome region on 15q11→q13. Cytogenet Cell Genet 87:125–131 - PubMed
-
- Buiting K, Saitoh S, Gross S, Dittrich B, Schwartz S, Nicholls RD, Horsthemke B (1995) Inherited microdeletions in the Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes define an imprinting centre on human chromosome 15. Nat Genet 9:395–400 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

