Complexes between the LKB1 tumor suppressor, STRAD alpha/beta and MO25 alpha/beta are upstream kinases in the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade
- PMID: 14511394
- PMCID: PMC333410
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-4924-2-28
Complexes between the LKB1 tumor suppressor, STRAD alpha/beta and MO25 alpha/beta are upstream kinases in the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade
Abstract
Background: The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) cascade is a sensor of cellular energy charge that acts as a 'metabolic master switch' and inhibits cell proliferation. Activation requires phosphorylation of Thr172 of AMPK within the activation loop by upstream kinases (AMPKKs) that have not been identified. Recently, we identified three related protein kinases acting upstream of the yeast homolog of AMPK. Although they do not have obvious mammalian homologs, they are related to LKB1, a tumor suppressor that is mutated in the human Peutz-Jeghers cancer syndrome. We recently showed that LKB1 exists as a complex with two accessory subunits, STRAD alpha/beta and MO25 alpha/beta.
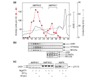
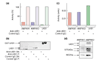
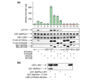
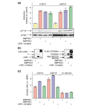
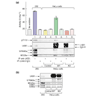
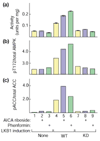
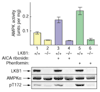
Results: We report the following observations. First, two AMPKK activities purified from rat liver contain LKB1, STRAD alpha and MO25 alpha, and can be immunoprecipitated using anti-LKB1 antibodies. Second, both endogenous and recombinant complexes of LKB1, STRAD alpha/beta and MO25 alpha/beta activate AMPK via phosphorylation of Thr172. Third, catalytically active LKB1, STRAD alpha or STRAD beta and MO25 alpha or MO25 beta are required for full activity. Fourth, the AMPK-activating drugs AICA riboside and phenformin do not activate AMPK in HeLa cells (which lack LKB1), but activation can be restored by stably expressing wild-type, but not catalytically inactive, LKB1. Fifth, AICA riboside and phenformin fail to activate AMPK in immortalized fibroblasts from LKB1-knockout mouse embryos.
Conclusions: These results provide the first description of a physiological substrate for the LKB1 tumor suppressor and suggest that it functions as an upstream regulator of AMPK. Our findings indicate that the tumors in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome could result from deficient activation of AMPK as a consequence of LKB1 inactivation.
Figures
Comment in
-
A new protein kinase cascade.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Apr;15(4):223. doi: 10.1038/nrm3771. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24622616 No abstract available.
References
-
- Coven DL, Hu X, Cong L, Bergeron R, Shulman GI, Hardie DG, Young LH. Physiologic role of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in the heart: graded activation during exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003;285:E629–E636. - PubMed
-
- Hawley SA, Davison M, Woods A, Davies SP, Beri RK, Carling D, Hardie DG. Characterization of the AMP-activated protein kinase kinase from rat liver, and identification of threonine-172 as the major site at which it phosphorylates and activates AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:27879–27887. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.44.27879. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

