Dio-Sensimedia: a novel culture medium for rapid detection of extended spectrum beta-lactamases
- PMID: 14511397
- PMCID: PMC222987
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-3-22
Dio-Sensimedia: a novel culture medium for rapid detection of extended spectrum beta-lactamases
Abstract
Background: Resistance to contemporary broad-spectrum beta-lactams, mediated by extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBL), is an increasing problem worldwide. Many of the emerging antimicrobial resistance problems of this decade have been characterized by difficulty in the recognition of resistance in the laboratory, particularly by rapid susceptibility test methods. The plasmid-encoded ESBL represent such a resistance phenomenon that is difficult to recognize. We compared Dio-Sensimedia-ES (DSM-ES; Diomed, Istanbul, Turkey) and Mueller-Hinton (MH) agar in the double-disk synergy test (DDST) as a novel rapid system for detecting ESBL directly from bacterial culture.
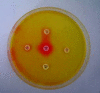
Methods: Sixty ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates cultured from blood (30), endotracheal aspirates (20), urine (5) and pus (5), as well as 40 Escherichia coli isolates cultured from endotracheal aspirates (15), urine (10), blood (8) and pus (7) were studied. Isolates positive for ESBL by the combined disk tests were tested with the DDST using MH and DSM-ES agar to detect ESBL-mediated resistance in K. pneumoniae and E. coli. DSM-ES agar was also used to determine the susceptibility of Enterobacteriaceae and staphylococci.
Results: Among 60 ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae isolates, 59 (98.3%) were identified as ESBL-positive by the DDST using MH, and 58 (96.6%), using DSM-ES agar. Of 40 ESBL-producing E. coli isolates, 38 (95%) were ESBL-positive by the DDST on MH agar, and 37 (92.5%), on DSM-ES agar. The average incubation period required for ESBL detection by the DDST on DSM-ES agar was 4 hours.
Conclusions: Since the DDST results were available within 4 hours when DSM-ES agar was used, the use of this media may significantly lower the length of hospital stay, the total cost for patient care and even the mortality rate by facilitating early treatment against ESBL-producing organisms.
Figures

References
-
- Shah PW, Stille W. Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae strains more susceptible to cefoxitin than to third generation cephalosporins [Letter] J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983;11:597–8. - PubMed
-
- Jarlier V, Nicolas MH, Fournier G, Philippon A. Extended broad-spectrum beta-lactamases conferring transferable resistance to newer beta-lactam agents in Enterobacteriaceae : Hospital prevalence and susceptibility pattern. Rev Infect Dis. 1988;10:867–78. - PubMed
-
- Jacoby GA, Medeiros AA, O'Brien TF, Pinto ME, Jiang H. Broad-spectrum, transmissible beta-lactamases. N Engl J Med. 1988;319:723–4. - PubMed
-
- Diekema DJ, Pfaller MA, Jones RN, and the SENTRY participants Group (Americas) et al. Survey of bloodstream infections due to gram-negative bacilli: Frequency of occurence and antimicrobial susceptibility of isolates collected in the United States, Canada, and Latin America for the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program 1997. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29:595–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

