Molecular dissection of the vaccinia virus I7L core protein proteinase
- PMID: 14512576
- PMCID: PMC225000
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.20.11279-11283.2003
Molecular dissection of the vaccinia virus I7L core protein proteinase
Abstract
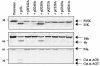
The vaccinia virus I7L gene product is predicted to be a cysteine proteinase and is demonstrated in this study to be responsible for cleavage of each of the three major core protein precursors (P4a, P4b, and P25K) in vivo. Mutagenesis of the putative catalytic triad of I7L or of the cleavage sites in the core protein precursors inhibits processing. A truncated protein lost the ability to cleave the core protein precursors.
Figures

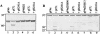
References
-
- Andres, G., A. Alejo, C. Simon-Mateo, and M. L. Salas. 2001. African swine fever virus protease, a new viral member of the SUMO-1 specific-protease family. J. Biol. Chem. 276:780-787. - PubMed
-
- Condit, R. C., A. Motyczka, and G. Spizz. 1983. Isolation, characterization, and physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutants of vaccinia virus. Virology 128:429-443. - PubMed
-
- Freimuth, P., and C. W. Anderson. 1993. Human adenovirus serotype 12 virion precursors pMu and pVI are cleaved at amino-terminal and carboxy-terminal sites that conform to the adenovirus 2 endoproteinase cleavage consensus sequence. Virology 193:348-355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

