Cooperative domains define a unique host cell-targeting signal in Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes
- PMID: 14514891
- PMCID: PMC218770
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2133080100
Cooperative domains define a unique host cell-targeting signal in Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes
Abstract
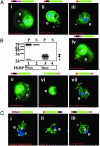
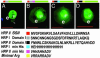
When the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum infects an erythrocyte, it resides in a parasitophorous vacuole and remarkably exports proteins into the periphery of its host cell. Two of these proteins, the histidine-rich proteins I and II (PfHRPI and PfHRPII), are exported to the erythrocyte cytoplasm. PfHRPI has been linked to cell-surface "knobby" protrusions that mediate cerebral malaria and are a frequent cause of death. PfHRPII has been implicated in (i) the production of hemozoin, the black pigment associated with disease, as well as (ii) interactions with the erythrocyte cytoskeleton. Here we show that a tripartite signal that is comprised of an endoplasmic reticulum-type signal sequence followed by a bipartite vacuolar translocation signal derived from HRPII and HRPI exports GFP from the parasitophorous vacuole to the host cytoplasm. The bipartite vacuolar translocation signal is comprised of unique, peptidic (approximately equal to 40-aa) sequences. A domain within it contains the signal for export to "cleft" transport intermediates in the host erythrocyte and may thereby regulate the pathway of export to the host cytoplasm. A signal for posttranslational, vacuolar exit of proteins has hitherto not been described in eukaryotic secretion.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeting malaria parasite proteins to the erythrocyte.Trends Parasitol. 2005 Sep;21(9):399-402. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2005.07.006. Trends Parasitol. 2005. PMID: 16046185 Review.
-
A host-targeting signal in virulence proteins reveals a secretome in malarial infection.Science. 2004 Dec 10;306(5703):1934-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1102737. Science. 2004. PMID: 15591203
-
Correct promoter control is needed for trafficking of the ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen to the host cytosol in transfected malaria parasites.Infect Immun. 2004 Oct;72(10):6095-105. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.6095-6105.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15385514 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicle-mediated trafficking of parasite proteins to the host cell cytosol and erythrocyte surface membrane in Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes.Int J Parasitol. 2001 Oct;31(12):1381-91. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(01)00256-9. Int J Parasitol. 2001. PMID: 11566305 Review.
-
PTEX component HSP101 mediates export of diverse malaria effectors into host erythrocytes.Nature. 2014 Jul 31;511(7511):592-5. doi: 10.1038/nature13574. Epub 2014 Jul 16. Nature. 2014. PMID: 25043010 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The role of KAHRP domains in knob formation and cytoadherence of P falciparum-infected human erythrocytes.Blood. 2006 Jul 1;108(1):370-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-11-4624. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16507777 Free PMC article.
-
Host targeting of virulence determinants and phosphoinositides in blood stage malaria parasites.Trends Parasitol. 2012 Dec;28(12):555-62. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2012.09.004. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Trends Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 23084821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal-mediated export of proteins from the malaria parasite to the host erythrocyte.J Cell Biol. 2005 Nov 21;171(4):587-92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200508051. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16301328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Plasmodium gene family encoding Maurer's cleft membrane proteins: structural properties and expression profiling.Genome Res. 2004 Jun;14(6):1052-9. doi: 10.1101/gr.2126104. Epub 2004 May 12. Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15140830 Free PMC article.
-
Export of malaria proteins requires co-translational processing of the PEXEL motif independent of phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding.Nat Commun. 2016 Feb 1;7:10470. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10470. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 26832821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chasis, J. A., Prenant, M., Leung, A. & Mohandas, N. (1989) Blood 74, 1112-1120. - PubMed
-
- Schrier, S. L. (1985) Clin. Haematol. 14, 1-12. - PubMed
-
- Gratzer, W. R. & Dluzewski, A. R. (1993) Semin. Hematol. 30, 232-247. - PubMed
-
- Holder, A. A., Guevara Patino, J. A., Uthaipibull, C., Syed, S. E., Ling, I. T., Scott-Finnigan, T. & Blackman, M. J. (1999) Parassitologia (Rome) 41, 409-414. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (2002) Roll Back Malaria Information Sheet (World Health Organization, Geneva).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

