Co-trimoxazole-sensitive, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Israel, 1988-1997
- PMID: 14519258
- PMCID: PMC3016776
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0909.020666
Co-trimoxazole-sensitive, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Israel, 1988-1997
Abstract
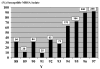
Among bloodstream methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates from adult patients in a single hospital, susceptibility to co-trimoxazole increased progressively from 31% in 1988 to 92% in 1997 (p<0.0001). If also observed in other institutions, these findings should encourage the performance of a clinical trial of sufficient size to compare co-trimoxazole to vancomycin in treating MRSA infections.
Figures
Comment in
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Pakistan, 1996-2003.Emerg Infect Dis. 2004 Sep;10(9):1691-2. doi: 10.3201/eid1009.030844. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15503408 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance standards for antimicrobials disk susceptibility tests. Approved standard M2-A4. Villanova (PA): The Committee; 1990.
-
- ATC index with DDDs. WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Oslo; 2001.
-
- Denis O, Deplano A, Nonhoff C, de Ryck R, Rottieres S, Hendricks E, et al. Molecular epidemiology and antimicrobial susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Belgian hospitals: 2001. 42nd Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. Abstract. San Diego: American Society for Microbiology; 2002. p. 305.
-
- Hiramatsu K, Okuma K, Ma XX, Yamamoto M, Hori S, Kapi M. New trends in Staphylococcus aureus infections: glycopeptide resistance in hospital and methicillin resistance in the community. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2002;4:407–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
