Modified de Gramont with oxaliplatin in the first-line treatment of advanced colorectal cancer
- PMID: 14520437
- PMCID: PMC2394314
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601237
Modified de Gramont with oxaliplatin in the first-line treatment of advanced colorectal cancer
Abstract
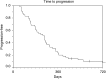
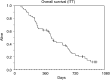
We previously reported high activity for oxaliplatin and a modified de Gramont regimen (OxMdG) in a single centre study of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. We now report results with a further 56 patients treated at 14 centres. Low rates of grade 3 and 4 toxicity were seen, with no toxic deaths. Objective response rates were CR/PR=53%; NC=34.7%; PD=12.2%. Median time to progression was 8.3 months and overall survival was 14.5 months. This regimen is more convenient than those based around the conventional de Gramont regimen but is highly active and well tolerated; it forms part of a current UK MRC phase 3 trial.
Figures
References
-
- Bern MM, Lockich JJ, Wallach SE, Bothe A Jr, Benotti PN, Arkin CF, Greco FA, Huberman M, Moore C (1990) Very low doses of warfarin can prevent thrombosis in central venous catheters. Annal Intern Med 112: 423–428 - PubMed
-
- de Gramont A, Bosset JF, Milan C, Rougier P, Bouche O, Etienne PL, Morvan F, Louvet C, Guillot T, Francois E, Bedenne L (1997) Randomised trial comparing monthly low-dose leucovorin and fluorouracil bolus with bimonthly high-dose leucovorin and fluorouracil bolus plus continuous infusion for advanced colorectal cancer: a French Intergroup Study. J Clin Oncol 15: 808–815 - PubMed
-
- de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J, Boni C, Cortes-Funes H, Cervantes A, Freyer G, Papamichael D, Le Bail N, Louvet C, Hendler D, de Braud F, Wilson C, Morvan F, Bonetti A (2000) Leucovorin and 5-fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 18: 2938–2947 - PubMed
-
- Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD, Navarro M, James RD, Karasek P, Jandik P, Iveson T, Carmichael J, Alakl M, Gruia G, Awad L, Rougier P (2000) Irinotecan combined with fluorouracil alone as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet 355: 1041–1047 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials