Membranous location of EGFR immunostaining is associated with good prognosis in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 14520458
- PMCID: PMC2394310
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601241
Membranous location of EGFR immunostaining is associated with good prognosis in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a key factor in tumorigenesis. The association between EGFR expression and prognosis in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is not clear. In our study of 134 RCCs, the cellular location of immunostaining was evaluated and patients with EGFR-positive tumours with prominent membranous staining had a good prognosis. Their overall survival was significantly longer (P=0.004) than that of patients with either EGFR-negative tumours or with mainly cytoplasmic staining. However, further studies on the different EGFR expression patterns in RCC are needed to clarify their role in the progression of the disease.
Figures
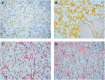
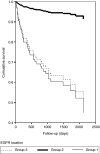
Comment in
-
Is membranous location of EGFR or EGFRvIII immunostaining associated with good prognosis in renal cell carcinoma?Br J Cancer. 2005 Nov 28;93(11):1316. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602843. Br J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16234813 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Carpenter G (2000) The EGF receptor: a nexus for trafficking and signalling. BioEssays 22: 697–707 - PubMed
-
- Fuhrman SA, Lasky LC, Limas C (1982) Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 6: 655–663 - PubMed
-
- Gomella LG, Anglard P, Sargent ER, Robertson CN, Kasid A, Linehan WM (1989) Epidermal growth factor receptor gene analysis in renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 143: 191–193 - PubMed
-
- Hirvikoski P, Kumpulainen EJ, Virtaniemi JA, Helin HJ, Rantala I, Johansson RT, Juhola M, Kosma V-M (1998) Cytoplasmic accumulation of alpha-catenin is associated with aggressive features in laryngeal squamous-cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 79: 546–550 - PubMed
-
- Hofmockel G, Riess S, Bassukas ID, Dämmrich J (1997) Epidermal growth factor family and renal cell carcinoma: expression and prognostic impact. Eur Urol 31: 478–484 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

