GLUT1 and CAIX as intrinsic markers of hypoxia in bladder cancer: relationship with vascularity and proliferation as predictors of outcome of ARCON
- PMID: 14520462
- PMCID: PMC2394309
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601260
GLUT1 and CAIX as intrinsic markers of hypoxia in bladder cancer: relationship with vascularity and proliferation as predictors of outcome of ARCON
Abstract
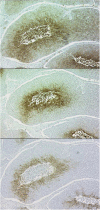
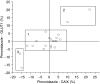
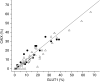
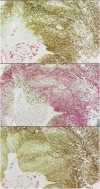
Glucose transporter-1 protein (GLUT1) and carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) are regulated by hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) and have been studied as putative intrinsic cellular markers for hypoxia. This study directly compares CAIX and GLUT1 with pimonidazole binding in a prospective series of bladder cancer patients and also studies the prognostic significance of the markers, in combination with vascularity and proliferation, in a retrospective series of bladder cancer patients treated in a phase II trial of radical radiotherapy with carbogen and nicotinamide (ARCON). A total of 21 patients with a diagnosis of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder received 0.5 g m(-2) pimonidazole. Serial tumour sections were stained for pimonidazole, GLUT1 and CAIX and compared. Tissue sections obtained from a series of 64 patients previously treated for invasive bladder cancer using ARCON were stained for GLUT1 and CAIX together with Ki-67 and CD31/34. There was a good geographical colocalisation of both intrinsic markers with pimonidazole and a highly significant agreement in individual patients; correlation coefficients were 0.82 (P=0.0001) for GLUT1 and 0.74 (P<0.0001) for CAIX. In both series of patients, the intrinsic hypoxia markers were highly correlated with each other and a correlation with proliferation was also evident in the retrospective study. In univariate and multivariate analyses, GLUT1 and CAIX were independent predictors for overall and cause specific survival. The hypoxia markers did not predict for local control or metastases-free survival although higher Ki-67 indices showed a trend towards local failure. The data suggest that both hypoxia modification and accelerated treatment may be valid treatment options in bladder cancer.
Figures
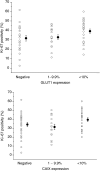
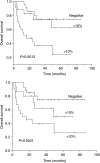
References
-
- Airley R, Loncaster J, Davidson S, Bromley M, Roberts S, Patterson A, Hunter R, Stratford I, West C (2001) Glucose transporter glut-1 expression correlates with tumor hypoxia and predicts metastasis-free survival in advanced carcinoma of the cervix. Clin Cancer Res 7: 928–934 - PubMed
-
- Airley RE, Loncaster J, Raleigh JA, Harris AL, Davidson SE, Hunter RD, West CM, Stratford IJ (2003) GLUT-1 and CAIX as intrinsic markers of hypoxia in carcinoma of the cervix: relationship to pimonidazole binding. Int J Cancer 104: 85–91 - PubMed
-
- Baer S, Casaubon L, Schwartz MR, Marcogliese A, Younes M (2002) Glut3 expression in biopsy specimens of laryngeal carcinoma is associated with poor survival. Laryngoscope 112: 393–396 - PubMed
-
- Beasley NJ, Leek R, Alam M, Turley H, Cox GJ, Gatter K, Millard P, Fuggle S, Harris AL (2002) Hypoxia–inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in head and neck cancer: relationship to tumor biology and treatment outcome in surgically resected patients. Cancer Res 62: 2493–2497 - PubMed
-
- Brizel DM, Sibley GS, Prosnitz LR, Scher RL, Dewhirst MW (1997) Tumor hypoxia adversely affects the prognosis of carcinoma of the head and neck. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 38: 285–289 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

