Evidence of progenitor cells of glandular and myoepithelial cell lineages in the human adult female breast epithelium: a new progenitor (adult stem) cell concept
- PMID: 14521517
- PMCID: PMC6495658
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2184.36.s.1.7.x
Evidence of progenitor cells of glandular and myoepithelial cell lineages in the human adult female breast epithelium: a new progenitor (adult stem) cell concept
Abstract
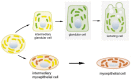
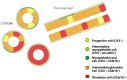
Although experimental data clearly confirm the existence of self-renewing mammary stem cells, the characteristics of such progenitor cells have never been satisfactorily defined. Using a double immunofluorescence technique for simultaneous detection of the basal cytokeratin 5, the glandular cytokeratins 8/18 and the myoepithelial differentiation marker smooth muscle actin (SMA), we were able to demonstrate the presence of CK5+ cells in human adult breast epithelium. These cells have the potential to differentiate to either glandular (CK8/18+) or myoepithelial cells (SMA+) through intermediary cells (CK5+ and CK8/18+ or SMA+). We therefore proceeded on the assumption that the CK5+ cells are phenotypically and behaviourally progenitor (committed adult stem) cells of human breast epithelium. Furthermore, we furnish evidence that most of these progenitor cells are located in the luminal epithelium of the ductal lobular tree. Based on data obtained in extensive analyses of proliferative breast disease lesions, we have come to regard usual ductal hyperplasia as a progenitor cell-derived lesion, whereas most breast cancers seem to evolve from differentiated glandular cells. Double immunofluorescence experiments provide a new tool to characterize phenotypically progenitor (adult stem) cells and their progenies. This model has been shown to be of great value for a better understanding not only of normal tissue regeneration but also of proliferative breast disease. Furthermore, this model provides a new tool for unravelling further the regulatory mechanisms that govern normal and pathological cell growth.
Figures
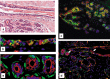
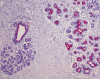
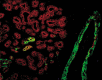
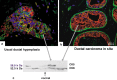
Similar articles
-
Ck5-positive cells are precursor cells of glandular and myoepithelial cell lineages in the human breast epithelium. A new cell concept as a basis for a better understanding of proliferative breast disease?Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 2005;89:45-7. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 2005. PMID: 18035671
-
Common adult stem cells in the human breast give rise to glandular and myoepithelial cell lineages: a new cell biological concept.Lab Invest. 2002 Jun;82(6):737-46. doi: 10.1097/01.lab.0000017371.72714.c5. Lab Invest. 2002. PMID: 12065684
-
Usual ductal hyperplasia of the breast is a committed stem (progenitor) cell lesion distinct from atypical ductal hyperplasia and ductal carcinoma in situ.J Pathol. 2002 Dec;198(4):458-67. doi: 10.1002/path.1241. J Pathol. 2002. PMID: 12434415
-
[Anatomy of the breast].Pathologe. 2009 Feb;30(1):6-12. doi: 10.1007/s00292-008-1102-3. Pathologe. 2009. PMID: 19184024 Review. German.
-
Epithelial progenitor cell lines as models of normal breast morphogenesis and neoplasia.Cell Prolif. 2003 Oct;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):33-44. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2184.36.s.1.4.x. Cell Prolif. 2003. PMID: 14521514 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Of mice and women: a comparative tissue biology perspective of breast stem cells and differentiation.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2015 Jun;20(1-2):51-62. doi: 10.1007/s10911-015-9341-4. Epub 2015 Aug 19. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2015. PMID: 26286174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eccrine ductal and acrosyringeal differentiation of the breast epithelium--a lesion associated with some metaplastic breast carcinomas.Virchows Arch. 2006 Nov;449(5):565-71. doi: 10.1007/s00428-006-0281-7. Epub 2006 Oct 3. Virchows Arch. 2006. PMID: 17016720
-
Cytokeratin 5 positive cells represent a steroid receptor negative and therapy resistant subpopulation in luminal breast cancers.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Jul;128(1):45-55. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-1078-6. Epub 2010 Jul 28. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 20665103 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Contractility and Invasion Potential of Two Canine Mammary Tumor Cell Lines.Front Vet Sci. 2017 Sep 12;4:149. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2017.00149. eCollection 2017. Front Vet Sci. 2017. PMID: 28955712 Free PMC article.
-
CAMK1D amplification implicated in epithelial-mesenchymal transition in basal-like breast cancer.Mol Oncol. 2008 Dec;2(4):327-39. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2008.09.004. Epub 2008 Oct 2. Mol Oncol. 2008. PMID: 19383354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Böcker WJ, Bier B, Freytag G, Brömmelkamp B, Jarasch E‐D, Edel G, Dockhorn‐Dworniczak B, Schmid KW (1992a) An immunohistochemical study of the breast using antibodies to basal and luminal keratins, alpha‐smooth muscle actin, vimentin, collagen IV and laminin. Part I: normal breast and benign proliferative lesions. Virchows Arch. A 421, 315. - PubMed
-
- Böcker WJ, Bier B, Freytag G, Brömmelkamp B, Jarasch E‐D, Edel G, Dockhorn‐Dworniczak B, Schmid KW (1992b) An immunohistochemical study of the breast using antibodies to basal and luminal keratins, alpha‐smooth muscle actin, vimentin, collagen IV and laminin. Part II: Epitheliosis and ductal carcinoma in situ . Virchows Arch. A 421, 323. - PubMed
-
- Boecker W, Moll R, Poremba C, Holland R, Van Diest PJ, Dervan P, Buerger H, Wai D, Diallo RI, Brandt B, Herbst H, Schmidt A, Lerch MM, Buchwallow IB (2002) Common adult stem cells in the human breast give rise to glandular and myoepithelial cell lineages: a new cell biological concept. Lab. Invest. 82, 737. - PubMed
-
- Brittan M, Wright NA (2002) Gastrointestinal stem cells. J. Path. 197, 492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

