Efflux of human and mouse amyloid beta proteins 1-40 and 1-42 from brain: impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 14522007
- PMCID: PMC3389491
- DOI: 10.1016/s0306-4522(03)00474-3
Efflux of human and mouse amyloid beta proteins 1-40 and 1-42 from brain: impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
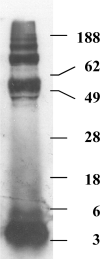
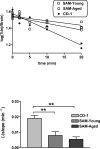
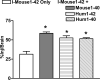
Brain to blood transport is believed to be a major determinant of the amount of amyloid beta protein (AbetaP) found in brain. Impaired efflux has been suggested as a mechanism by which AbetaP can accumulate in the CNS and so lead to Alzheimer's disease (AD). To date, however, no study of the efflux of the form of AbetaP most relevant to AD, AbetaP1-42, has been conducted, even though a single amino acid substitution in AbetaP can greatly alter efflux. Here, we examined the efflux of AbetaP mouse1-42, mouse1-40, human1-42, and human1-40 in young CD-1, young senesence accelerated mouse (SAM) P8, and aged SAMP8 mice. The SAMP8 mouse with aging spontaneously overproduces AbetaP and develops cognitive impairments reversed by AbetaP-directed antibody or phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotide. CD-1 mice transported all forms of AbetaP, although mouse1-42 and human1-40 were transported faster than the other forms. There was a decrease in the saturable transport of mouse1-42 in SAMP8 mice regardless of age. Efflux of mouse1-40 and human1-42 was only by a non-saturable mechanism in young SAMP8 mice and their efflux was totally absent in aged SAMP8 mice. These differences in the efflux of the various forms of AbetaP among the three groups of mice supports the hypothesis that impaired efflux is an important factor in the accumulation of AbetaP in the CNS.
Figures
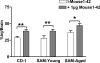
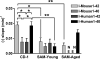
References
-
- Bacskai BJ, Kajdasz ST, Christie RH, Carter C, Games D, Seubert P, Schenk D, Hyman BT. Imaging of amyloid-β deposits in brains of living mice permits direct observation of clearance of plaques with immunotherapy. Nature Medicine. 2001;7:369–372. - PubMed
-
- Bading JR, Yamada S, Mackic JB, Kirkman L, Miller C, Calero M, Ghiso J, Frangione B, Zlokovic BV. Brain clearance of Alzheimer's amyloid-ß040 in the squirrel monkey: A SPECT study in a primate model of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. J Drug Targeting. 2002;10:359–368. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Broadwell RD. Blood to brain and brain to blood passage of native horseradish peroxidase, wheat germ agglutinin and albumin: pharmacokinetic and morphological assessments. J Neurochem. 1994;62:2404–2419. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, DiPalma CR, Farrell CL. Impaired transport of leptin across the blood-brain barrier in obesity. Peptides. 1999;20:1341–1345. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Farr SA, Butt W, Kumar VB, Franko MW, Morley JE. Delivery across the blood-brain barrier of antisense directed againt amyloid β: reversal of learning and memory deficits in mice overexpressing amyloid precursor protein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;297:1113–1121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

