Diabetes, microvascular complications, and cardiovascular complications: what is it about glucose?
- PMID: 14523035
- PMCID: PMC198532
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI19902
Diabetes, microvascular complications, and cardiovascular complications: what is it about glucose?
Abstract
Glycemic control is the primary mediator of diabetic microvascular complications and also contributes to macrovascular complications. A new study (see related article beginning on page 1049) reveals a previously unrecognized association between oxidant activation of poly(ADP ribose) polymerase (PARP) and upregulation of known mediators of glycemic injury. Inhibitors of PARP may have potential therapeutic roles in the prevention of diabetic complications.
Figures
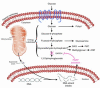
Comment on
-
Inhibition of GAPDH activity by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activates three major pathways of hyperglycemic damage in endothelial cells.J Clin Invest. 2003 Oct;112(7):1049-57. doi: 10.1172/JCI18127. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 14523042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyle JP, et al. Projection of diabetes burden through 2050: impact of changing demography and disease prevalence in the U.S. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:1936–1940. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin SM, Valdez R, Geiss LS, Rolka DB, Narayan KM. Estimated number of adults with prediabetes in the U.S. in 2000: opportunities for prevention. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:645–649. - PubMed
-
- The Diabetes ControlComplications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993;329:977–986. - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33) Lancet. 1998;352:837–853. - PubMed
-
- Hanson RL, Imperatore G, Bennett PH, Knowler WC. Components of the “metabolic syndrome” and incidence of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2002;51:3120–3127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

