Regulatory functions of CD8+CD28- T cells in an autoimmune disease model
- PMID: 14523041
- PMCID: PMC198520
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI17935
Regulatory functions of CD8+CD28- T cells in an autoimmune disease model
Abstract
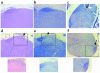
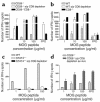
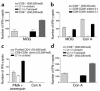
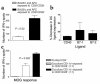
CD8+ T cell depletion renders CD28-deficient mice susceptible to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). In addition, CD8-/-CD28-/- double-knockout mice are susceptible to EAE. These findings suggest a role for CD8+ T cells in the resistance of CD28-deficient mice to disease. Adoptive transfer of CD8+CD28- T cells into CD8-/- mice results in significant suppression of disease, while CD8+CD28+ T cells demonstrate no similar effect on the clinical course of EAE in the same recipients. In vitro, CD8+CD28- but not CD8+CD28+ T cells suppress IFN-gamma production of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-specific CD4+ T cells. This suppression requires cell-to-cell contact and is dependent on the presence of APCs. APCs cocultured with CD8+CD28- T cells become less efficient in inducing a T cell-dependent immune response. Such interaction prevents upregulation of costimulatory molecules by APCs, hence decreasing the delivery of these signals to CD4+ T cells. These are the first data establishing that regulatory CD8+CD28- T cells occur in normal mice and play a critical role in disease resistance in CD28-/- animals.
Figures
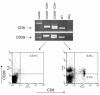
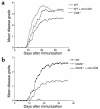
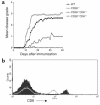
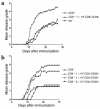
References
-
- Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, et al. CD28 costimulation is crucial for the development of spontaneous autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 1999;162:4490–4495. - PubMed
-
- Perrin PJ, Lavi E, Rumbley CA, Zekavat SA, Phillips SM. Experimental autoimmune meningitis: a novel neurological disease in CD28-deficient mice. Clin. Immunol. 1999;91:41–49. - PubMed
-
- Girvin AM, et al. A critical role for B7/CD28 costimulation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: a comparative study using costimulatory molecule-deficient mice and monoclonal antibody blockade. J. Immunol. 2000;164:136–143. - PubMed
-
- Karpus WJ, et al. An important role for the chemokine macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha in the pathogenesis of the T cell-mediated autoimmune disease, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 1995;155:5003–5010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

