The tissue plasminogen activator-plasminogen proteolytic cascade accelerates amyloid-beta (Abeta) degradation and inhibits Abeta-induced neurodegeneration
- PMID: 14523088
- PMCID: PMC6740393
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-26-08867.2003
The tissue plasminogen activator-plasminogen proteolytic cascade accelerates amyloid-beta (Abeta) degradation and inhibits Abeta-induced neurodegeneration
Abstract
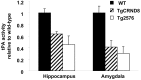
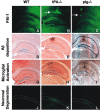
Accumulation of the amyloid-beta (Abeta) peptide depends on both its generation and clearance. To better define clearance pathways, we have evaluated the role of the tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)-plasmin system in Abeta degradation in vivo. In two different mouse models of Alzheimer's disease, chronically elevated Abeta peptide in the brain correlates with the upregulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) and inhibition of the tPA-plasmin system. In addition, Abeta injected into the hippocampus of mice lacking either tPA or plasminogen persists, inducing PAI-1 expression and causing activation of microglial cells and neuronal damage. Conversely, Abeta injected into wild-type mice is rapidly cleared and does not cause neuronal degeneration. Thus, the tPA-plasmin proteolytic cascade aids in the clearance of Abeta, and reduced activity of this system may contribute to the progression of Alzheimer's disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Amyloid beta soluble forms and plasminogen activation system in Alzheimer's disease: Consequences on extracellular maturation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and therapeutic implications.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019 Mar;25(3):303-313. doi: 10.1111/cns.13082. Epub 2018 Nov 6. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019. PMID: 30403004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impacts of aging and amyloid-β deposition on plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in the Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res. 2015 Feb 9;1597:159-67. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.11.042. Epub 2014 Nov 29. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25454795
-
Amyloid-beta levels are significantly reduced and spatial memory defects are rescued in a novel neuroserpin-deficient Alzheimer's disease transgenic mouse model.J Neurochem. 2011 Sep;118(5):928-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07359.x. Epub 2011 Jul 18. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 21689108
-
Knockout of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 gene reduces amyloid beta peptide burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Aging. 2011 Jun;32(6):1079-89. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.06.003. Epub 2009 Jul 14. Neurobiol Aging. 2011. PMID: 19604604 Free PMC article.
-
The probable role of tissue plasminogen activator/neuroserpin axis in Alzheimer's disease: a new perspective.Acta Neurol Belg. 2024 Apr;124(2):377-388. doi: 10.1007/s13760-023-02403-x. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Acta Neurol Belg. 2024. PMID: 37917293 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
2,5-Hexanedione induced apoptosis in rat spinal cord neurons and VSC4.1 cells via the proNGF/p75NTR and JNK pathways.Biosci Rep. 2021 Apr 30;41(4):BSR20204264. doi: 10.1042/BSR20204264. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33792642 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrinogen and altered hemostasis in Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;32(3):599-608. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-120820. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22869464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aging, Cellular Senescence, and Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 11;23(4):1989. doi: 10.3390/ijms23041989. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulations of the neuronal trafficking of tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) influences glutamate release.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Jan 18;14(1):34. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05543-9. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 36650132 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid beta soluble forms and plasminogen activation system in Alzheimer's disease: Consequences on extracellular maturation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and therapeutic implications.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019 Mar;25(3):303-313. doi: 10.1111/cns.13082. Epub 2018 Nov 6. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019. PMID: 30403004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akassoglou K, Yu WM, Akpinar P, Strickland S ( 2002) Fibrin inhibits peripheral nerve remyelination by regulating Schwann cell differentiation. Neuron 33: 861-875. - PubMed
-
- Baranes D, Lederfein D, Huang YY, Chen M, Bailey CH, Kandel ER ( 1998) Tissue plasminogen activator contributes to the late phase of LTP and to synaptic growth in the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway. Neuron 21: 813-825. - PubMed
-
- Beher D, Wrigley JD, Nadin A, Evin G, Masters CL, Harrison T, Castro JL, Shearman MS ( 2001) Pharmacological knock-down of the presenilin 1 heterodimer by a novel gamma-secretase inhibitor: implications for presenilin biology. J Biol Chem 276: 45394-45402. - PubMed
-
- Chen ZL, Strickland S ( 1997) Neuronal death in the hippocampus is promoted by plasmin-catalyzed degradation of laminin. Cell 91: 917-925. - PubMed
-
- Chishti MA, Yang DS, Janus C, Phinney AL, Horne P, Pearson J, Strome R, Zuker N, Loukides J, French J, Turner S, Lozza G, Grilli M, Kunicki S, Morissette C, Paquette J, Gervais F, Bergeron C, Fraser PE, Carlson GA, George-Hyslop PS, Westaway D ( 2001) Early-onset amyloid deposition and cognitive deficits in transgenic mice expressing a double mutant form of amyloid precursor protein 695. J Biol Chem 276: 21562-21570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
