Functional and phylogenetic analyses of a conserved regulatory program in the phloem of minor veins
- PMID: 14526110
- PMCID: PMC281618
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.027714
Functional and phylogenetic analyses of a conserved regulatory program in the phloem of minor veins
Abstract
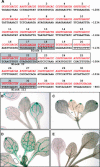
The minor-vein phloem of mature leaves is developmentally and physiologically distinct from the phloem in the rest of the vascular system. Phloem loading of transport sugars occurs in the minor veins, and consistent with this, galactinol synthase is expressed in the minor veins of melon (Cucumis melo) as part of the symplastic-loading mechanism that operates in this species. A galactinol synthase promoter from melon drives gene expression in the minor-vein companion cells of both transgenic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) and Arabidopsis. Neither of these plants use galactinol in the phloem-loading process, implying that the promoter responds to a minor-vein-specific regulatory cascade that is highly conserved across a broad range of eudicotyledons. Detailed analysis of this promoter by truncation and mutagenesis identified three closely coupled sequences that unambiguously modulate tissue specificity. These sequences cooperate in a combinatorial fashion: two promote expression throughout the vascular system of the plant, whereas the third functions to repress expression in the larger bundles. In a complementary approach, phylogenetic footprinting was used to obtain single-nucleotide resolution of conserved sites in orthologous promoters from diverse members of the Cucurbitaceae. This comparative analysis confirmed the importance of the closely coupled sites but also revealed other highly conserved sequences that may modulate promoter strength or contribute to expression patterns outside of the phloem. The conservation of this regulatory design among species that phloem load by different mechanisms supports a model for organismal development in which tissues and cell types are controlled by relatively ancient and conserved paradigms but expression of genes influencing final form and function are relatively plastic.
Figures
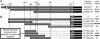

References
-
- Arguello-Astorga G, Herrera-Estrella L (1998) Evolution of light-regulated plant promoters. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49: 525–555 - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidmam JG, Smith JA, editors (1995) Short Protocols in Molecular Biology, Ed 3. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

