Functional map and domain structure of MET, the product of the c-met protooncogene and receptor for hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor
- PMID: 14528000
- PMCID: PMC218709
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2034936100
Functional map and domain structure of MET, the product of the c-met protooncogene and receptor for hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor
Abstract
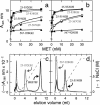
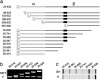
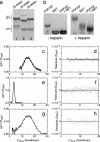
Little is known about the large ectodomain of MET, the product of the c-met protooncogene and receptor for hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF). Here, we establish by deletion mutagenesis that the HGF/SF and heparin-binding sites of MET are contained within a large N-terminal domain spanning the alpha-chain (amino acids 25-307) and the first 212 amino acids of the beta-chain (amino acids 308-519). Neither the cystine-rich domain (amino acids 520-561) nor the C-terminal half of MET (amino acids 562-932) bind HGF/SF or heparin directly. The MET ectodomain, which behaves as a rod-shaped monomer with a large Stokes radius in solution, binds HGF/SF in the absence or presence of heparin, and forms a stable HGF/SF-heparin-MET complex with 1:1:1 stoichiometry. We also show that the ligand-binding domain adopts a beta-propeller fold, which is similar to the N-terminal domain of alphaV integrin, and that the C-terminal half contains four Ig domains (amino acids 563-654, 657-738, 742-836, and 839-924) of the unusual structural E set, which could be modeled on bacterial enzymes. Our studies provide 3D models and a functional map of the MET ectodomain. They have broad implications for structure-function of the MET receptor and the related semaphorin and plexin proteins.
Figures


References
-
- Blume-Jensen, P. & Hunter, T. (2001) Nature 411, 355–365. - PubMed
-
- Harpaz, Y. & Chothia, C. (1994) J. Mol. Biol. 238, 528–539. - PubMed
-
- Cooper, C. S., Blair, D. G., Oskarsson, M. K., Tainsky, M. A., Eader, L. A. & Vande Woude, G. F. (1984) Cancer Res. 44, 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Bottaro, D. P., Rubin, J. S., Faletto, D. L., Chan, A. M., Kmiecik, T. E., Vande Woude, G. F. & Aaronson, S. A. (1991) Science 251, 802–804. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

