Scavenger receptor BI (SR-BI) clustered on microvillar extensions suggests that this plasma membrane domain is a way station for cholesterol trafficking between cells and high-density lipoprotein
- PMID: 14528013
- PMCID: PMC307555
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-06-0445
Scavenger receptor BI (SR-BI) clustered on microvillar extensions suggests that this plasma membrane domain is a way station for cholesterol trafficking between cells and high-density lipoprotein
Abstract
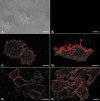
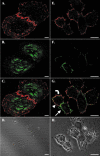
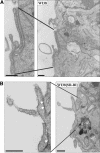
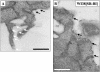
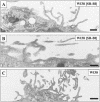
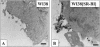
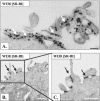
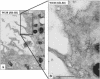
Receptor-mediated trafficking of cholesterol between lipoproteins and cells is a fundamental biological process at the organismal and cellular levels. In contrast to the well-studied pathway of LDL receptor-mediated endocytosis, little is known about the trafficking of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol by the HDL receptor, scavenger receptor BI (SR-BI). SR-BI mediates HDL cholesteryl ester uptake in a process in which HDL lipids are selectively transferred to the cell membrane without the uptake and degradation of the HDL particle. We report here the cell surface locale where the trafficking of HDL cholesterol occurs. Fluorescence confocal microscopy showed SR-BI in patches and small extensions of the cell surface that were distinct from sites of caveolin-1 expression. Electron microscopy showed SR-BI in patches or clusters primarily on microvillar extensions of the plasma membrane. The organization of SR-BI in this manner suggests that this microvillar domain is a way station for cholesterol trafficking between HDL and cells. The types of phospholipids in this domain are unknown, but SR-BI is not strongly associated with classical membrane rafts rich in detergent-resistant saturated phospholipids. We speculate that SR-BI is in a more fluid membrane domain that will favor rapid cholesterol flux between the membrane and HDL.
Figures



References
-
- Acton, S., Rigotti, A., Landschulz, K.T., Xu, S., Hobbs, H.H., and Krieger, M. (1996). Identification of scavenger receptor SR-BI as a high density lipoprotein receptor. Science 271, 518-520. - PubMed
-
- Arai, T., Wang, N., Bezouevski, M., Welch, C., and Tall, A.R. (1999). Decreased atherosclerosis in heterozygous low density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice expressing the scavenger receptor BI transgene. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 2366-2371. - PubMed
-
- Babitt, J., Trigatti, B., Rigotti, A., Smart, E., Anderson, R.G.W., Xu, S., and Krieger, M. (1997). Murine SR-BI, a high density lipoprotein receptor that mediates selective lipid uptake, is N-glycosylated and fatty acylated and colocalizes with plasma membrane caveolae. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 13242-13249. - PubMed
-
- Braun, A., Trigatti, B.L., Post, M.J., Sato, K., Simons, M., Edelberg, J.M., Rosenberg, R.D., Schrenzel, M., and Krieger, M. (2002). Loss of SR-BI expression leads to the early onset of occlusive atherosclerotic coronary artery disease, spontaneous myocardial infarctions, severe cardiac dysfunction, and premature death in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circ. Res. 90, 270-276. - PubMed
-
- Brown, D., and London, E. (1998). Structure and origin of ordered lipid domains in biological membranes. J. Membr. Biol. 164, 103-114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

