Constitutive cytokine mRNAs mark natural killer (NK) and NK T cells poised for rapid effector function
- PMID: 14530376
- PMCID: PMC2194220
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030630
Constitutive cytokine mRNAs mark natural killer (NK) and NK T cells poised for rapid effector function
Abstract
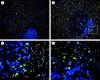
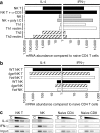
Natural killer (NK) and NK T cells are tissue lymphocytes that secrete cytokines rapidly upon stimulation. Here, we show that these cells maintain distinct patterns of constitutive cytokine mRNAs. Unlike conventional T cells, NK T cells activate interleukin (IL)-4 and interferon (IFN)-gamma transcription during thymic development and populate the periphery with both cytokine loci previously modified by histone acetylation. Similarly, NK cells transcribe and modify the IFN-gamma gene, but not IL-4, during developmental maturation in the bone marrow. Lineage-specific patterns of cytokine transcripts predate infection and suggest evolutionary selection for invariant but distinct types of effector responses among the earliest responding lymphocytes.
Figures
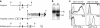


References
-
- Bendelac, A., M.N. Rivera, S.H. Park, and J.H. Roark. 1997. Mouse CD1-specific NK1 T cells: development, specificity, and function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15:535–562. - PubMed
-
- Cerwenka, A., and L.L. Lanier. 2001. Natural killer cells, viruses and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 1:41–49. - PubMed
-
- Arase, H., E.S. Mocarski, A.E. Campbell, A.B. Hill, and L.L. Lanier. 2002. Direct recognition of cytomegalovirus by activating and inhibitory NK cell receptors. Science. 296:1323–1326. - PubMed
-
- French, A.R., and W.M. Yokoyama. 2003. Natural killer cells and viral infections. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 15:45–51. - PubMed
-
- Biron, C.A., K.S. Byron, and J.L. Sullivan. 1989. Severe herpesvirus infections in an adolescent without natural killer cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 320:1731–1735. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

