Inhibition of NF-kappaB by ZAS3, a zinc-finger protein that also binds to the kappaB motif
- PMID: 14530385
- PMCID: PMC218753
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2133048100
Inhibition of NF-kappaB by ZAS3, a zinc-finger protein that also binds to the kappaB motif
Abstract
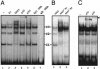
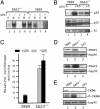
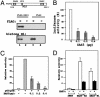
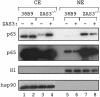
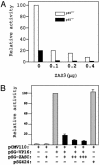
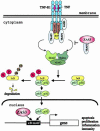
The ZAS proteins are large zinc-finger transcriptional proteins implicated in growth, signal transduction, and lymphoid development. Recombinant ZAS fusion proteins containing one of the two DNA-binding domains have been shown to bind specifically to the kappaB motif, but the endogenous ZAS proteins or their physiological functions are largely unknown. The kappaB motif, GGGACTTTCC, is a gene regulatory element found in promoters and enhancers of genes involved in immunity, inflammation, and growth. The Rel family of NF-kappaB, predominantly p65.p50 and p50.p50, are transcription factors well known for inducing gene expression by means of interaction with the kappaB motif during acute-phase responses. A functional link between ZAS and NF-kappaB, two distinct families of kappaB-binding proteins, stems from our previous in vitro studies that show that a representative member, ZAS3, associates with TRAF2, an adaptor molecule in tumor necrosis factor signaling, to inhibit NF-kappaB activation. Biochemical and genetic evidence presented herein shows that ZAS3 encodes major kappaB-binding proteins in B lymphocytes, and that NF-kappaB is constitutively activated in ZAS3-deficient B cells. The data suggest that ZAS3 plays crucial functions in maintaining cellular homeostasis, at least in part by inhibiting NF-kappaB by means of three mechanisms: inhibition of nuclear translocation of p65, competition for kappaB gene regulatory elements, and repression of target gene transcription.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of p50/p65 heterodimer of transcription factor NF-kappaB bound to DNA.Nature. 1998 Jan 22;391(6665):410-3. doi: 10.1038/34956. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9450761
-
Reciprocal regulation of nuclear factor kappa B and its inhibitor ZAS3 after peripheral nerve injury.BMC Neurosci. 2006 Jan 12;7:4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-7-4. BMC Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16409637 Free PMC article.
-
A biophysical characterisation of factors controlling dimerisation and selectivity in the NF-kappaB and NFAT families.J Mol Biol. 2004 Jun 18;339(5):1059-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.03.083. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15178248
-
ZAS: C2H2 zinc finger proteins involved in growth and development.Gene Expr. 2002;10(4):137-52. doi: 10.3727/000000002783992479. Gene Expr. 2002. PMID: 12173742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specification of DNA binding activity of NF-kappaB proteins.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009 Oct;1(4):a000067. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000067. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009. PMID: 20066093 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel HIVEP2 Variants in Patients with Intellectual Disability.Mol Syndromol. 2019 Jul;10(4):195-201. doi: 10.1159/000499060. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Mol Syndromol. 2019. PMID: 31602191 Free PMC article.
-
Preservation of intestinal structural integrity by zinc is independent of metallothionein in alcohol-intoxicated mice.Am J Pathol. 2004 Jun;164(6):1959-66. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63756-X. Am J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15161632 Free PMC article.
-
Schnurri 3 promotes Th2 cytokine production during the late phase of T-cell antigen stimulation.Eur J Immunol. 2022 Jul;52(7):1077-1094. doi: 10.1002/eji.202149633. Epub 2022 May 11. Eur J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35490426 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB regulation: the nuclear response.J Cell Mol Med. 2009 Apr;13(4):631-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00632.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19438970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel estrogen target gene ZAS3 is overexpressed in systemic lupus erythematosus.Mol Immunol. 2013 May;54(1):23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.10.026. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23178823 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

