The HLA-DQ2 gene dose effect in celiac disease is directly related to the magnitude and breadth of gluten-specific T cell responses
- PMID: 14530392
- PMCID: PMC218768
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2135229100
The HLA-DQ2 gene dose effect in celiac disease is directly related to the magnitude and breadth of gluten-specific T cell responses
Abstract
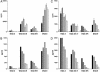
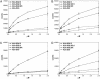
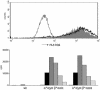
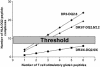
In patients with celiac disease, inflammatory T cell responses to HLA-DQ2-bound gluten peptides are thought to cause disease. Two types of HLA-DQ2 molecules exist, termed HLA-DQ2.5 and HLA-DQ2.2. Whereas HLA-DQ2.5 predisposes to celiac disease, HLA-DQ2.2 does not. We now provide evidence that the disease-associated HLA-DQ2.5 molecule presents a large repertoire of gluten peptides, whereas the non-disease-associated HLA-DQ2.2 molecule can present only a subset of these. Moreover, gluten presentation by HLA-DQ2 homozygous antigen-presenting cells was superior to presentation by HLA-DQ2/non-DQ2 heterozygous antigen-presenting cells in terms of T cell proliferation and cytokine secretion. Gluten presentation by HLA-DQ2.5/2.2 heterozygous antigen-presenting cells induced intermediate T cell stimulation. These results correlated with peptide binding to the antigen-presenting cells. Finally, we demonstrate that HLA-DQ trans dimers formed in HLA-DQ2.5/2.2 heterozygous individuals have properties identical with HLA-DQ2.5 dimers. Our findings explain the strongly increased risk of disease development for HLA-DQ2.5 homozygous and HLA-DQ2.2/2.5 heterozygous individuals, and they are indicative of a quantitative model for disease development, where HLA-DQ expression and the available number of T cell-stimulatory gluten peptides are critical limiting factors. This model may have important implications for disease prevention.
Figures
References
-
- van de Wal, Y., Kooy, Y. M. C., Drijfhout, J. W., Amons, R. & Koning, F. (1996) Immunogenetics 44, 246-253. - PubMed
-
- Vartdal, F., Johansen, B. H., Friede, T., Thorpe, C. J., Stevanovic, S., Eriksen, J. E., Sletten, K., Thorsby, E., Rammensee, H. G. & Sollid, L. M. (1996) Eur. J. Immunol. 26, 2764-2772. - PubMed
-
- Molberg, O., McAdam, S. N., Korner, R., Quarsten, H., Kristiansen, C., Madsen, L., Fugger, L., Scott, H., Noren, O., Roepstorff, P., et al. (1998) Nat. Med. 4, 713-717. - PubMed
-
- van de Wal, Y., Kooy, Y., van Veelen, P., Pena, S., Mearin, L., Papadopoulos, G. & Koning, F. (1998) J. Immunol. 161, 1585-1588. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

