Multiplex real-time PCR method to identify Shiga toxin genes stx1 and stx2 and Escherichia coli O157:H7/H- serotype
- PMID: 14532101
- PMCID: PMC201207
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.10.6327-6333.2003
Multiplex real-time PCR method to identify Shiga toxin genes stx1 and stx2 and Escherichia coli O157:H7/H- serotype
Abstract
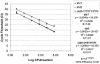
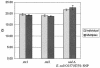
A multiplex real-time PCR method to simultaneously detect the stx1 and stx2 genes of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and a unique conserved single-nucleotide polymorphism in the E. coli O157:H7/H- uidA gene has been developed. There is more than 98.6% sensitivity and 100% specificity for all three gene targets based on a panel of 138 isolates. The PCR efficiencies were >/= 1.89, and as few as 6 CFU/reaction could be detected.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed, S., and M. Donaghy. 1998. An outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in central Scotland, p. 59-65. In J. B. Kaper and A. D. O'Brien (ed.), Escherichia coli O157:H7 and other Shiga toxin-producing E. coli strains. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
-
- Bustin, S. A. 2000. Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 25:169-193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

