Mitochondrial translocation contact sites: separation of dynamic and stabilizing elements in formation of a TOM-TIM-preprotein supercomplex
- PMID: 14532110
- PMCID: PMC213786
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg532
Mitochondrial translocation contact sites: separation of dynamic and stabilizing elements in formation of a TOM-TIM-preprotein supercomplex
Abstract
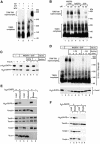
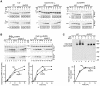
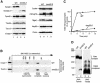
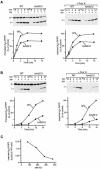
Preproteins with N-terminal presequences are imported into mitochondria at translocation contact sites that include the translocase of the outer membrane (TOM complex) and the presequence translocase of the inner membrane (TIM23 complex). Little is known about the functional cooperation of these translocases. We have characterized translocation contact sites by a productive TOM-TIM-preprotein supercomplex to address the role of three translocase subunits that expose domains to the intermembrane space (IMS). The IMS domain of the receptor Tom22 is required for stabilization of the translocation contact site supercomplex. Surprisingly, the N-terminal segment of the channel Tim23, which tethers the TIM23 complex to the outer membrane, is dispensable for both protein import and generation of the TOM-TIM supercomplex. Tim50, with its large IMS domain, is crucial for generation but not for stabilization of the supercomplex. Thus, Tim50 functions as a dynamic factor and the IMS domain of Tom22 represents a stabilizing element in formation of a productive translocation contact site supercomplex.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A presequence- and voltage-sensitive channel of the mitochondrial preprotein translocase formed by Tim23.Nat Struct Biol. 2001 Dec;8(12):1074-82. doi: 10.1038/nsb726. Nat Struct Biol. 2001. PMID: 11713477
-
Mitochondrial presequence translocase: switching between TOM tethering and motor recruitment involves Tim21 and Tim17.Cell. 2005 Mar 25;120(6):817-29. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.01.011. Cell. 2005. PMID: 15797382
-
Tom22 is a multifunctional organizer of the mitochondrial preprotein translocase.Nature. 1999 Sep 30;401(6752):485-9. doi: 10.1038/46802. Nature. 1999. PMID: 10519552
-
Protein import into mitochondria.IUBMB Life. 2001 Sep-Nov;52(3-5):101-12. doi: 10.1080/15216540152845894. IUBMB Life. 2001. PMID: 11798021 Review.
-
Mitochondrial preprotein translocases as dynamic molecular machines.FEMS Yeast Res. 2006 Sep;6(6):849-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2006.00134.x. FEMS Yeast Res. 2006. PMID: 16911507 Review.
Cited by
-
Revisiting trends on mitochondrial mega-channels for the import of proteins and nucleic acids.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2017 Feb;49(1):75-99. doi: 10.1007/s10863-016-9662-z. Epub 2016 May 5. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2017. PMID: 27146409 Review.
-
Towards a molecular mechanism underlying mitochondrial protein import through the TOM and TIM23 complexes.Elife. 2022 Jun 8;11:e75426. doi: 10.7554/eLife.75426. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35674314 Free PMC article.
-
Tim23-Tim50 pair coordinates functions of translocators and motor proteins in mitochondrial protein import.J Cell Biol. 2009 Jan 12;184(1):129-41. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200808068. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19139266 Free PMC article.
-
Two distinct membrane potential-dependent steps drive mitochondrial matrix protein translocation.J Cell Biol. 2017 Jan 2;216(1):83-92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201607066. Epub 2016 Dec 23. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28011846 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Functions of Tim50, a Component of the Mitochondrial Inner Membrane Protein Translocase.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 21;22(15):7779. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157779. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360547 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abe Y., Shodai,T., Muto,T., Mihara,K., Torii,H., Nishikawa,S., Endo,T. and Kohda,D. (2000) Structural basis of presequence recognition by the mitochondrial protein import receptor Tom20. Cell, 100, 551–560. - PubMed
-
- Bauer M.F., Sirrenberg,C., Neupert,W. and Brunner,M. (1996) Role of Tim23 as voltage sensor and presequence receptor in protein import into mitochondria. Cell, 87, 33–41. - PubMed
-
- Bauer M.F., Hofmann,S., Neupert,W. and Brunner,M. (2000) Protein translocation into mitochondria: the role of TIM complexes. Trends Cell Biol., 10, 25–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

