Survival during treatment with tumour necrosis factor blocking agents in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 14532145
- PMCID: PMC1766750
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.62.suppl_2.ii30
Survival during treatment with tumour necrosis factor blocking agents in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
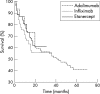
Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) blocking agents are an important advance in the clinical treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). They were introduced into clinical practice while limited safety information was available. This means that intensive monitoring is needed early in the life cycle of these new drugs. Setting up large cohort studies to monitor efficacy, safety, and tolerability in long term use of these so-called biological agents will provide information about the consequences of using TNF blocking agents in chronic rheumatic disease like RA. Currently, a Dutch multicentre registry on biological agents in RA is being set up. This study aimed at investigating the efficacy and toxicity of TNF blocking agents in patients with RA at one participating academic centre by a drug survival analysis. Since 1997 230 patients with RA at the centre have been treated with TNF blocking agents for the first time (94 with adalimumab, 120 with infliximab, and 16 with etanercept). No differences in drug survival between the three TNF blocking agents were found despite the diversity in selection and patient numbers. Adverse events which occurred, leading to discontinuation, were similar to those from previous reports.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical