The transmembrane semaphorin Sema4D/CD100, an inhibitor of axonal growth, is expressed on oligodendrocytes and upregulated after CNS lesion
- PMID: 14534257
- PMCID: PMC6740837
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-27-09229.2003
The transmembrane semaphorin Sema4D/CD100, an inhibitor of axonal growth, is expressed on oligodendrocytes and upregulated after CNS lesion
Abstract
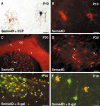
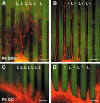
Semaphorins are a family of secreted and membrane-bound proteins, known to regulate axonal pathfinding. Sema4D, also called CD100, was first isolated in the immune system where it is involved in B and T cell activation. We found that in the mouse, Sema4D is expressed in cells throughout the CNS white matter, with a peak during the myelination period. Double-labeling experiments with different markers of oligodendrocyte lineage such as olig1, olig2, platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha, and proteolipid protein showed that Sema4D was expressed selectively by oligodendrocytes and myelin. The presence of Sema4D in myelin was confirmed using Western blot. Sema4D expression in myelinating oligodendrocytes was further observed using neuron-oligodendrocyte cocultures. Moreover, using stripe assay, we found that Sema4D is strongly inhibitory for postnatal sensory and cerebellar granule cell axons. This prompted us to examine whether Sema4D expression is modified after CNS injury. At 8 d after spinal cord lesions, Sema4D expression was strongly upregulated in oligodendrocytes at the periphery of the lesion. Sema4D-positive cells were not colabeled with the astrocyte marker GFAP, with the microglial and macrophagic marker isolectin B4, or with NG2, a marker of oligodendrocyte precursors. This upregulation was transient because from 1 month after the lesion, Sema4D expression was back to its normal level. These results indicate that Sema4D is a novel inhibitory factor for axonal regeneration expressed in myelin.
Figures





References
-
- Bartholdi D, Schwab ME ( 1998) Oligodendroglial reaction following spinal cord injury in rat: transient upregulation of MBP mRNA. Glia 23: 278-284. - PubMed
-
- Bartsch U, Bandtlow CE, Schnell L, Bartsch S, Spillmann AA, Rubin BP, Hillenbrand R, Montag D, Schwab ME, Schachner M ( 1995) Lack of evidence that myelin-associated glycoprotein is a major inhibitor of axonal regeneration in the CNS. Neuron 15: 1375-1381. - PubMed
-
- Bottenstein J, Hayashi I, Hutchings S, Masui H, Mather J, McClure DB, Ohasa S, Rizzino A, Sato G, Serrero G, Wolfe R, Wu R ( 1979) The growth of cells in serum-free hormone-supplemented media. Methods Enzymol 58: 94-109. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury EJ, Moon LD, Popat RJ, King VR, Bennett GS, Patel PN, Fawcett JW, McMahon SB ( 2002) Chondroitinase ABC promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Nature 16: 636-640. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
