Nicotine is highly effective at producing desensitization of rat alpha4beta2 neuronal nicotinic receptors
- PMID: 14555718
- PMCID: PMC2343639
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.053447
Nicotine is highly effective at producing desensitization of rat alpha4beta2 neuronal nicotinic receptors
Abstract
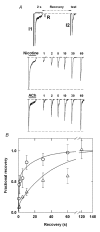
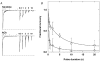
We examined desensitization by acetylcholine (ACh) and nicotine at the rat alpha4beta2 neuronal nicotinic receptor stably expressed in HEK cells. For both agonists, the decay in response due to desensitization ('onset') was best fitted by the sum of two exponentials with the fast component dominant at concentrations > 1 microM. The time constants for onset were similar for both agonists, and showed little concentration dependence over the range of 0.1-100 microM. Recovery from desensitization also showed two exponential components. In contrast to the similarity in onset, nicotine produced longer lasting desensitization, resulting from an increase in the proportion of receptors in the slowly recovering population and from an increase in the time constant for the slow recovery process. The proportion of receptors in the slowly recovering population increased as the duration of the desensitizing pulse increased. Desensitization was also induced by low concentrations of agonist, with no apparent macroscopic response. A 100 s application of 10 nM nicotine desensitized 70 % of the peak response, while 100 s of 10 nM ACh desensitized only 15 %. At higher concentrations of agonist, which result in a macroscopic response, desensitization in the absence of activation also can occur. Nicotine is a very potent and efficacious desensitizing agent at this neuronal nicotinic receptor.
Figures



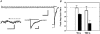
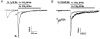


References
-
- Benwell MEM, Balfour DJK, Anderson JM. Evidence that tobacco smoking increases the density of (−)-[3H]nicotine binding sites in human brain. J Neurochem. 1988;50:1243–1247. - PubMed
-
- Bufler J, Franke C, Witzemann V, Ruppersberg JP, Merlitze S, Dudel J. Desensitization of embryonic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neurosci Lett. 1993;152:77–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

