Cis-acting elements and DNA-binding proteins involved in CO2-responsive transcriptional activation of Cah1 encoding a periplasmic carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
- PMID: 14555782
- PMCID: PMC219052
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.026492
Cis-acting elements and DNA-binding proteins involved in CO2-responsive transcriptional activation of Cah1 encoding a periplasmic carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Abstract
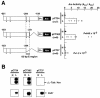
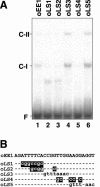
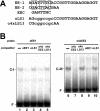
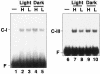
Expression of Cah1, encoding a periplasmic carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Dangeard, is activated when cells are exposed to low-CO2 conditions (0.04% [v/v]) in light. By using an arylsulfatase reporter gene, a regulatory region essential for the transcriptional activation of Cah1 was delimited to a 63-bp fragment between -293 and -231 relative to the transcription start site. Linker-scan analysis of the 63-bp region identified two enhancer elements, EE-1 (AGATTTTCACCGGTTGGAAGGAGGT) and EE-2 (CGACTTACGAA). Gel mobility shift assays indicated that nuclear extracts purified from cells grown under low-CO2 conditions in light contained DNA-binding proteins specifically interacting with EE-1 and EE-2. Gel mobility shift assays using mutant oligonucleotide probes revealed that the protein binding to EE-1 preferentially recognized a 9-bp sequence stretch (AGATTTTCA) of EE-1, containing a conserved sequence motif named EEC, GANTTNC, which is also present in EE-2. The EE-1- and EE-2-binding proteins interacted with the EECs contained in both of the two enhancer elements in vitro. Four EECs in the 5'-upstream region from -651 to -231 of Cah1 played a central role in the transcriptional activation of Cah1 under low-CO2 conditions. These EEC-binding proteins were present even in cells grown under high-CO2 conditions (5% [v/v]) or in the dark when Cah1 is not activated. On the basis of these results, the relationship between the transcriptional regulation of Cah1 and protein-binding to the enhancer elements in the 5'-upstream region of Cah1 is discussed.
Figures



References
-
- Abmayr SM, Workman JL (1997) Preparation of nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts from mammalian cells. In FM Ausubel, R Brent, RE Kingston, DD Moore, JG Seidman, JA Smith, K Struhl, eds, Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Current Protocols, New York, pp 12.1.1.1–12.1.9
-
- Aizawa K, Miyachi S (1986) Carbonic anhydrase and CO2 concentrating mechanisms in microalgae and cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39: 215–233
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1997) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley-Interscience, New York, pp 12.1.1–12.2.10
-
- Badger MR, Price GD (1994) The role of carbonic anhydrase in photosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 45: 369–392
-
- Chodosh LA (1997) Mobility shift DNA-binding assay using gell electrophoresis. In FM Ausubel, R Brent, RE Kingston, DD Moore, JG Seidman, JA Smith, K Struhl, eds, Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Current Protocols, New York, pp 12.2.1–12.2.10
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

