Adiponectin stimulates angiogenesis by promoting cross-talk between AMP-activated protein kinase and Akt signaling in endothelial cells
- PMID: 14557259
- PMCID: PMC4374490
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M310389200
Adiponectin stimulates angiogenesis by promoting cross-talk between AMP-activated protein kinase and Akt signaling in endothelial cells
Abstract
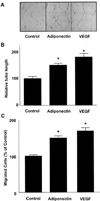
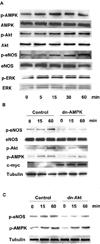
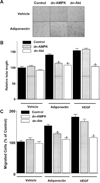
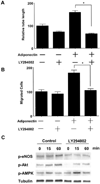
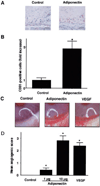
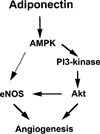
Adiponectin is an adipocyte-specific adipocytokine with anti-atherogenic and anti-diabetic properties. Here, we investigated whether adiponectin regulates angiogenic processes in vitro and in vivo. Adiponectin stimulated the differentiation of human umbilical vein endothelium cells (HUVECs) into capillary-like structures in vitro and functioned as a chemoattractant in migration assays. Adiponectin promoted the phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), protein kinase Akt/protein kinase B, and endothelial nitric oxide synthesis (eNOS) in HUVECs. Transduction with either dominant-negative AMPK or dominant-negative Akt abolished adiponectin-induced eNOS phosphorylation as well as adiponectin-stimulated HUVEC migration and differentiation. Dominant-negative AMPK also inhibited adiponectin-induced Akt phosphorylation, suggesting that AMPK is upstream of Akt. Dominant-negative Akt or the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002 blocked adiponectin-stimulated Akt and eNOS phosphorylation, migration, and differentiation without altering AMPK phosphorylation. Finally, adiponectin stimulated blood vessel growth in vivo in mouse Matrigel plug implantation and rabbit corneal models of angiogenesis. These data indicate that adiponectin can function to stimulate the new blood vessel growth by promoting cross-talk between AMP-activated protein kinase and Akt signaling within endothelial cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adiponectin stimulates production of nitric oxide in vascular endothelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 7;278(45):45021-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M307878200. Epub 2003 Aug 27. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12944390
-
Modulation by peroxynitrite of Akt- and AMP-activated kinase-dependent Ser1179 phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase.J Biol Chem. 2002 Sep 6;277(36):32552-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M204512200. Epub 2002 Jul 9. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12107173
-
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling in endothelial cells is essential for angiogenesis in response to hypoxic stress.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 15;278(33):31000-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300643200. Epub 2003 Jun 4. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12788940
-
Membrane estrogen receptor engagement activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase via the PI3-kinase-Akt pathway in human endothelial cells.Circ Res. 2000 Oct 13;87(8):677-82. doi: 10.1161/01.res.87.8.677. Circ Res. 2000. PMID: 11029403
-
Nitric oxide and angiogenesis.J Neurooncol. 2000 Oct-Nov;50(1-2):139-48. doi: 10.1023/a:1006431309841. J Neurooncol. 2000. PMID: 11245273 Review.
Cited by
-
Estrogen-related receptor alpha is an AMPK-regulated factor that promotes ischemic muscle revascularization and recovery in diet-induced obese mice.FASEB Bioadv. 2022 Jun 22;4(9):602-618. doi: 10.1096/fba.2022-00015. eCollection 2022 Sep. FASEB Bioadv. 2022. PMID: 36089981 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) by nitrated lipids in endothelial cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31056. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031056. Epub 2012 Feb 17. PLoS One. 2012. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2020 May 19;15(5):e0233408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233408. PMID: 22363546 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The role of adiponectin in cancer: a review of current evidence.Endocr Rev. 2012 Aug;33(4):547-94. doi: 10.1210/er.2011-1015. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Endocr Rev. 2012. PMID: 22547160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective suppression of endothelial cell apoptosis by the high molecular weight form of adiponectin.Circ Res. 2004 Mar 5;94(4):e27-31. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000119921.86460.37. Epub 2004 Jan 29. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 14752031 Free PMC article.
-
AMPK-induced activation of Akt by AICAR is mediated by IGF-1R dependent and independent mechanisms in acute lymphoblastic leukemia.J Mol Signal. 2010 Sep 23;5:15. doi: 10.1186/1750-2187-5-15. J Mol Signal. 2010. PMID: 20863384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM. Nature. 1994;372:425–432. - PubMed
-
- Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Science. 1993;259:87–91. - PubMed
-
- Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Kotani K, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Miura M, Fukuda Y, Takemura K, Tokunaga K, Matsuzawa Y. Nat. Med. 1996;2:800–803. - PubMed
-
- Trayhurn P, Beattie JH. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2001;60:329–339. - PubMed
-
- Maeda K, Okubo K, Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Matsubara K. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996;221:286–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

