Delay-dependent working memory impairment in young-adult and aged 5-HT1BKO mice as assessed in a radial-arm water maze
- PMID: 14557613
- PMCID: PMC218006
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.60103
Delay-dependent working memory impairment in young-adult and aged 5-HT1BKO mice as assessed in a radial-arm water maze
Abstract
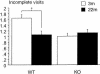
Serotonin (5-HT) plays a modulatory role in mnemonic functions, especially by interacting with the cholinergic system. The 5-HT1B receptor is a key target of this interaction. The 5-HT1B receptor knockout mice were found previously to exhibit a facilitation in hippocampal-dependent spatial reference memory learning. In the present study, we submitted mice to a delayed spatial working memory task, allowing the introduction of various delays between an exposure trial and a test trial. The 5-HT1BKO and wild-type mice learned the task in a radial-arm water maze (returning to the most recent presented arm containing the escape platform), and exhibited a high level of performance at delays of 0 and 5 min. However, at the delay of 60 min, only 5-HT1BKO mice exhibited an impairment. At a delay of 90 min, all mice were impaired. Treatment by scopolamine (0.8 mg/kg) induced the same pattern of performance in wild type as did the mutation for short (5 min, no impairment) and long (60 min, impairment) delays. The 22-month-old wild-type and knockout mice exhibited an impairment at short delays (5 and 15 min). The effect of the mutation affected both young-adult and aged mice at delays of 15, 30, and 60 min. Neurobiological data show that stimulation of the 5-HT1B receptor inhibits the release of acetylcholine in the hippocampus, but stimulates this in the frontal cortex. This dual function might, at least in part, explain the opposite effect of the mutation on reference memory (facilitation) and delay-dependent working memory (impairment). These results support the idea that cholinergic-serotonergic interactions play an important role in memory processes.
Figures

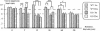

Similar articles
-
Spatial learning in the 5-HT1B receptor knockout mouse: selective facilitation/impairment depending on the cognitive demand.Learn Mem. 2003 Nov-Dec;10(6):466-77. doi: 10.1101/lm.60203. Learn Mem. 2003. PMID: 14657258 Review.
-
Analysis of the role of the 5-HT1B receptor in spatial and aversive learning in the rat.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003 Sep;28(9):1642-55. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300235. Epub 2003 Jul 2. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003. PMID: 12838273
-
Dissociation of cholinergic function in spatial and procedural learning in rats.Neuroscience. 2007 May 25;146(3):875-89. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.02.038. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17418958
-
Agmatine protects against scopolamine-induced water maze performance impairment and hippocampal ERK and Akt inactivation.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Apr;62(5-6):2018-23. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.12.031. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22248637
-
[Recent advances in studies of rat memory in the radial-arm maze].Yakubutsu Seishin Kodo. 1983 Dec;3(3):99-108. Yakubutsu Seishin Kodo. 1983. PMID: 6380133 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
HTR1B as a risk profile maker in psychiatric disorders: a review through motivation and memory.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010 Jan;66(1):5-27. doi: 10.1007/s00228-009-0724-6. Epub 2009 Oct 7. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19809810 Review.
-
Between destiny and disease: genetics and molecular pathways of human central nervous system aging.Prog Neurobiol. 2011 Feb;93(2):165-81. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.11.006. Epub 2010 Dec 2. Prog Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21130140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversal of spatial memory impairment by phosphodiesterase 3 inhibitor cilostazol is associated with reduced neuroinflammation and increased cerebral glucose uptake in aged male mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 21;13:1031637. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1031637. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36618932 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Behavioral Test Battery to Assess Learning and Memory in 129S6/Tg2576 Mice.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 25;11(1):e0147733. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147733. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26808326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amsel, A. 1993. Hippocampal function in the rat: Cognitive mapping or vicarious trial and error? Hippocampus 3: 251–256. - PubMed
-
- Bach, M.E., Barad, M., Son, H., Zhuo, M., Lu, Y.L., Shih, R., Mansuy, I., Hawkins, R.D., and Kandel, E.R. 1999. Age-related defects in spatial memory are correlated with defects in the late phase of hippocampal long-term potentiation in vitro and are attenuated by drugs that enhance the cAMP signaling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96: 5280–5285. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachevalier, J. and Mishkin, M. 1986. Visual recognition impairment follows ventromedial but not dorsolateral prefrontal lesions in monkeys. Behav. Brain Res. 20: 249–261. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, C.A. and McNaughton, B.L. 1985. An age comparison of the rates of acquisition and forgetting of spatial information in relation to long-term enhancement of hippocampal synapses. Behav. Neurosci. 99: 1040–1048. - PubMed
-
- Beatty, W.W. and Bierley, R.A. 1986. Scopolamine impairs encoding and retrieval of spatial working memory in rats. Physiol. Psychol. 14: 82–86.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
