Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 escape from RNA interference
- PMID: 14557638
- PMCID: PMC229317
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.21.11531-11535.2003
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 escape from RNA interference
Abstract
Sequence-specific degradation of mRNA by short interfering RNA (siRNA) allows the selective inhibition of viral proteins that are critical for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) replication. The aim of this study was to characterize the potency and durability of virus-specific RNA interference (RNAi) in cell lines that stably express short hairpin RNA (shRNA) targeting the HIV-1 transactivator protein gene tat. We found that the antiviral activity of tat shRNA was abolished due to the emergence of viral quasispecies harboring a point mutation in the shRNA target region. Our results suggest that, in order for RNAi to durably suppress HIV-1 replication, it may be necessary to target highly conserved regions of the viral genome. Alternatively, similar to present antiviral drug therapy paradigms, DNA constructs expressing multiple siRNAs need to be developed that target different regions of the viral genome, thereby reducing the probability of generating escape mutants.
Figures
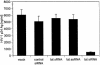
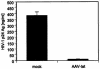
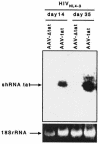

References
-
- Brummelkamp, T. R., R. Bernards, and R. Agami. 2002. Stable suppression of tumorigenicity by virus-mediated RNA interference. Cancer Cell 2:243-247. - PubMed
-
- Capodici, J., K. Kariko, and D. Weissman. 2002. Inhibition of HIV-1 infection by small interfering RNA-mediated RNA interference. J. Immunol. 169:5196-5201. - PubMed
-
- Gitlin, L., S. Karelsky, and R. Andino. 2002. Short interfering RNA confers intracellular antiviral immunity in human cells. Nature 418:430-434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

