Optimal induction of T-cell responses against hepatitis C virus E2 by antigen engineering in DNA immunization
- PMID: 14557645
- PMCID: PMC229347
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.21.11596-11602.2003
Optimal induction of T-cell responses against hepatitis C virus E2 by antigen engineering in DNA immunization
Abstract
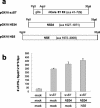
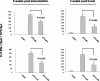
Although DNA immunization is a safe and efficient method for inducing cellular immune responses, it generates relatively weak and slow immune responses. Here, we investigated the effect of hepatitis C virus (HCV) antigen modifications on the induction of T-cell responses in DNA immunization. It is likely that the strength of T-cell responses has an inverse relationship with the length of the insert DNA. Interestingly, a mixture of several plasmids carrying each gene induced a higher level of T-cell responses than a single plasmid expressing a long polyprotein. Moreover, the presence of a transmembrane domain in HCV E2 resulted in stronger T-cell responses against E2 protein than its absence. Taken together, our results indicate that the tailored modifications of DNA-encoded antigens are capable of optimizing the induction of T-cell responses which is required for eliminating the cells chronically infected with highly variable viruses such as HCV and human immunodeficiency virus.
Figures



References
-
- Berzofsky, J. A., J. D. Ahlers, and I. M. Belyakov. 2001. Strategies for designing and optimizing new generation vaccines. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 1:209-219. - PubMed
-
- Boyle, J. S., C. Koniaras, and A. M. Lew. 1997. Influence of cellular location of expressed antigen on the efficacy of DNA vaccination: cytotoxic T lymphocyte and antibody responses are suboptimal when antigen is cytoplasmic after intramuscular DNA immunization. Int. Immunol. 9:1897-1906. - PubMed
-
- Caley, I. J., M. R. Betts, N. L. Davis, R. Swanstrom, J. A. Frelinger, and R. E. Johnston. 1999. Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus vectors expressing HIV-1 proteins: vector design strategies for improved vaccine efficacy. Vaccine 17:3124-3135. - PubMed
-
- Chastain, M., A. J. Simon, K. A. Soper, D. J. Holder, D. L. Montgomery, S. L. Sagar, D. R. Casimiro, and C. R. Middaugh. 2001. Antigen levels and antibody titers after DNA vaccination. J. Pharm. Sci. 90:474-484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

