Endovascular treatment strategy for direct carotid-cavernous fistulas resulting from rupture of intracavernous carotid aneurysms
- PMID: 14561604
- PMCID: PMC7976316
Endovascular treatment strategy for direct carotid-cavernous fistulas resulting from rupture of intracavernous carotid aneurysms
Abstract
Background and purpose: Reported treatments and outcomes in aneurysmal carotid-cavernous fistulas (CCFs) have been admixed with those of cases considered to be symptomatic of intracavernous aneurysm. However, aneurysmal CCFs have clinical features distinct from those of dural arteriovenous fistulas, and treatment strategies similar to those of traumatic CCF are required. We evaluated our experience in placing detachable balloons in the management of spontaneous CCFs due to rupture of an intracavernous aneurysm.
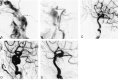
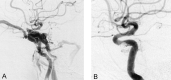
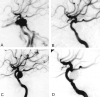
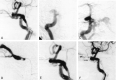
Methods: Six patients (one man, five women; mean age, 64.7 years) were treated for spontaneous direct CCF at our institution between 1995 and 2001. All patients presented with sudden ocular symptoms including exophthalmos, conjunctival injection, chemosis, and ocular motor palsies. Detachable latex balloons were used as the embolic material in five patients, and in one patient the cavernous sinus was packed transarterially with coils.
Results: All six patients were successfully treated by means of transarterial embolization, and symptoms improved within a week.
Conclusion: Although other techniques using a transvenous approach and/or detachable coils may also be useful, embolization with detachable balloons should be a safe and effective method to immediately occlude the fistula.
Figures


References
-
- Barrow DL, Spector RH, Braun IF, Landman JA, Tindall SC, Tindall GT. Classification and treatment of spontaneous carotid-cavernous sinus fistulas. J Neurosurg 1985;62:248–256 - PubMed
-
- Kanner AA, Maimon S, Rappaport ZH. Treatment of spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistula in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome by transvenous occlusion with Guglielmi detachable coils: case report. J Neurosurg 2000;93:689–692 - PubMed
-
- Debrun GM, Aletich VA, Miller NR, DeKeiser RJW. Three cases of spontaneous direct carotid cavernous fistulas associated with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV. Surg Neurol 1996;46:247–252 - PubMed
-
- d’Angelo VA, Monte V, Scialfa G, Fiumara E, Scotti G. Intracerebral venous hemorrhage in “high-risk” carotid-cavernous fistula. Surg Neurol 1988;30:387–390 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
