Recovery of renal function in dialysis patients
- PMID: 14563216
- PMCID: PMC270015
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-4-9
Recovery of renal function in dialysis patients
Abstract
Background: Although recovery of renal functions in dialysis dependent patients is estimated to be greater than 1%, there are no indicators that actually suggest such revival of renal function. Residual renal function in dialysis patients is unreliable and seldom followed. Therefore renal recovery (RR) in dialysis dependent patients may remain unnoticed. We present a group of dialysis dependent patients who regained their renal functions. The aim of this project is to determine any indicators that may identify the recovery of renal functions in dialysis dependent patients.
Methods: All the discharges from the chronic dialysis facilities were identified. Among these discharges deaths, transplants, voluntary withdrawals and transfers either to another modality or another dialysis facility were excluded in order to isolate the patients with RR. The dialysis flow sheets and medical records of these patients were subsequently reviewed.
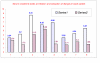
Results: Eight patients with a mean age of 53.8 +/- 6.7 years (+/- SEM) were found to have RR. Dialysis was initiated due to uremic symptoms in 6 patients and fluid overload in the remaining two. The patients remained dialysis dependent for 11.1 +/- 4.2 months. All these patients had good urine output and 7 had symptoms related to dialysis. Their mean pre-initiation creatinine and BUN levels were 5.21 +/- 0.6 mg/dl and 72.12 +/- 11.12 mg/dl, respectively. Upon discontinuation, they remained dialysis free for 19.75 +/- 5.97 months. The mean creatinine and BUN levels after cessation of dialysis were 2.85 +/- 0.57 mg/dl and 29.62 +/- 5.26 mg/dl, respectively, while the mean creatinine clearance calculated by 24-hour urine collection was 29.75 +/- 4.78 ml/min. One patient died due to HIV complications. One patient resumed dialysis after nine months. Remaining continue to enjoy a dialysis free life.
Conclusion: RR must be considered in patients with good urine output and unresolved acute renal failure. Dialysis intolerance may be an indicator of RR among such patients.
Figures
References
-
- Cohen DL, Townsend RR, Kobrin S, Genega EM, Tomaszewski JE, Fairman R. Dramatic recovery of renal function after 6 months of dialysis dependence following surgical correction of of total renal artery occlusion in a solitary functioning kidney. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;37:E7. - PubMed
-
- Cancarini GC, Pola A, Pezzotti G, Tardanico R, Cozzoli A, Cunico SC. Recovery of renal function after right nephrectomy, cavectomy and left renal vein ligation. J Nephrol. 2002;15:186–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical