The effect of recombinant human growth hormone and resistance training on IGF-I mRNA expression in the muscles of elderly men
- PMID: 14565994
- PMCID: PMC1664832
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.051722
The effect of recombinant human growth hormone and resistance training on IGF-I mRNA expression in the muscles of elderly men
Abstract
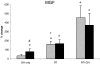
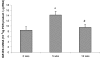
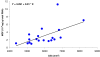
The expression of two isoforms of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I): mechano growth factor (MGF) and IGF-IEa were studied in muscle in response to growth hormone (GH) administration with and without resistance training in healthy elderly men. A third isoform, IGF-IEb was also investigated in response to resistance training only. The subjects (age 74 +/- 1 years, mean +/- S.E.M) were assigned to either resistance training with placebo, resistance training combined with GH administration or GH administration alone. Real-time quantitative RT-PCR was used to determine mRNA levels in biopsies from the vastus lateralis muscle at baseline, after 5 and 12 weeks in the three groups. GH administration did not change MGF mRNA at 5 weeks, but significantly increased IGF-IEa mRNA (237%). After 12 weeks, MGF mRNA was significantly increased (80%) compared to baseline. Five weeks of resistance training significantly increased the mRNA expression of MGF (163%), IGF-IEa (68%) and IGF-IEb (75%). No further changes were observed after 12 weeks. However, after 5 weeks of training combined with GH treatment, MGF mRNA increased significantly (456%) and IGF-IEa mRNA by (167%). No further significant changes were noted at 12 weeks. The data suggest that when mechanical loading in the form of resistance training is combined with GH, MGF mRNA levels are enhanced. This may reflect an overall up-regulation of transcription of the IGF-I gene prior to splicing.
Figures



References
-
- Adamo ML, Neuenschwander S, LeRoith D, Roberts CT., Jr Structure, expression, and regulation of the IGF-I gene. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;343:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Adams GR, McCue SA. Localized infusion of IGF-I results in skeletal muscle hypertrophy in rats. J Appl Physiol. 1998;84:1716–1722. - PubMed
-
- Andersen NB, Andreassen TT, Orskov H, Oxlund H. Growth hormone and mild exercise in combination increases markedly muscle mass and tetanic tension in old rats. Eur J Endocrinol. 2000;143:409–418. - PubMed
-
- Bamman MM, Ship JR, Jiang J, Gower BA, Hunter GR, Goodman A, et al. Mechanical load increases muscle IGF-1 and androgen receptor mRNA concentrations in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinal Metab. 2001;280:E383–E390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

