Properties of pacemaker potentials recorded from myenteric interstitial cells of Cajal distributed in the mouse small intestine
- PMID: 14565995
- PMCID: PMC2343623
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.051334
Properties of pacemaker potentials recorded from myenteric interstitial cells of Cajal distributed in the mouse small intestine
Abstract
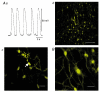
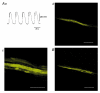
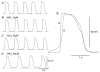
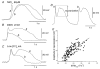
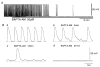
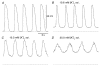
Recording of electrical responses from isolated small intestine of mice using conventional microelectrodes revealed two types of potential, a pacemaker potential and a slow wave, both with rapid rising primary components and following plateau components. The rate of rise and peak amplitude were greater for pacemaker potentials than for slow waves, and the plateau component was smaller in slow waves than in pacemaker potentials. Both potentials oscillated at a similar frequency (20-30 min-1). Unitary potentials often discharged during the interval between pacemaker potentials. Infusion of Lucifer Yellow allowed visualization of the recorded cells; pacemaker potentials were recorded from myenteric interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC-MY) while slow waves were recorded from circular smooth muscle cells. Pacemaker potentials were characterized as follows: the primary component was inhibited by Ni2+, Ca2+-free solution or depolarization with high-K+ solution, the plateau component was inhibited by 4,4'-diisothiocyanostilbene-2,2'-disulphonic acid (DIDS), an inhibitor of Ca2+-activated Cl- channels, low [Cl-]o solution or Ca2+-free solution, and the generation of potentials was abolished by co-application of Ni2+and DIDS or by chelating intracellular Ca2+ with 1,2-bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid acetoxymethyl ester (BAPTA-AM). These results indicate that in the mouse small intestine ICC-MY generate pacemaker potentials with two components in situ; the primary and plateau components may be generated by activation of voltage-dependent Ca2+-permeable channels and Ca2+-activated Cl- channels, respectively. Slow waves are generated in circular smooth muscles via electrotonic spread of pacemaker potentials. These properties of intestinal pacemaker potentials are considered essentially similar to those of gastric pacemaker potentials.
Figures
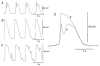




Similar articles
-
Components of pacemaker potentials recorded from the guinea pig stomach antrum.Pflugers Arch. 2002 Nov;445(2):202-17. doi: 10.1007/s00424-002-0884-z. Epub 2002 Oct 25. Pflugers Arch. 2002. PMID: 12457241
-
Development of pacemaker activity and interstitial cells of Cajal in the neonatal mouse small intestine.Dev Dyn. 1998 Nov;213(3):271-82. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199811)213:3<271::AID-AJA4>3.0.CO;2-R. Dev Dyn. 1998. PMID: 9825863
-
Characterization of slow waves generated by myenteric interstitial cells of Cajal of the rabbit small intestine.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Mar 1;308(5):G378-88. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00308.2014. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25540230 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological properties of gastric pacemaker potentials.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2003 Oct;39(5):163-73. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.39.163. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2003. PMID: 14695027 Review.
-
Cellular mechanisms of myogenic activity in gastric smooth muscle.Jpn J Physiol. 2000 Jun;50(3):289-301. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.50.289. Jpn J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 11016979 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle Function by Interstitial Cells.Physiology (Bethesda). 2016 Sep;31(5):316-26. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00006.2016. Physiology (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 27488743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atypical slow waves generated in gastric corpus provide dominant pacemaker activity in guinea pig stomach.J Physiol. 2005 Dec 1;569(Pt 2):459-65. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.097907. Epub 2005 Oct 13. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16223760 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical slow waves in the mouse oviduct are dependent on extracellular and intracellular calcium sources.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Dec;301(6):C1458-69. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00293.2011. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21881003 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of the Scn5a-encoded voltage-gated sodium channel NaV 1.5 in the rat jejunum.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016 Jan;28(1):64-73. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12697. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016. PMID: 26459913 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Cl- regulates electrical slow waves and setting of smooth muscle membrane potential by interstitial cells of Cajal in mouse jejunum.Exp Physiol. 2018 Jan 1;103(1):40-57. doi: 10.1113/EP086367. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Exp Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28971566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belzer V, Kobilo T, Rich A, Hanani M. Intercellular coupling among interstitial cells of Cajal in the guinea pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res. 2002;307:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Daniel EE, Wang YF, Cayabyab F. Role of gap junctions in structural arrangements of interstitial cells of Cajal and canine ileal smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1998;274:G1125–1141. - PubMed
-
- Dickens EJ, Edwards FR, Hirst GDS. Vagal inhibition in the antral region of guinea pig stomach. Am J Physiol. 2000;279:G388–399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

