Measuring Solution Viscosity and its Effect on Enzyme Activity
- PMID: 14569610
- PMCID: PMC154660
- DOI: 10.1251/bpo52
Measuring Solution Viscosity and its Effect on Enzyme Activity
Abstract
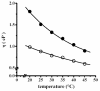
In proteins, some processes require conformational changes involving structural domain diffusion. Among these processes are protein folding, unfolding and enzyme catalysis. During catalysis some enzymes undergo large conformational changes as they progress through the catalytic cycle. According to Kramers theory, solvent viscosity results in friction against proteins in solution, and this should result in decreased motion, inhibiting catalysis in motile enzymes. Solution viscosity was increased by adding increasing concentrations of glycerol, sucrose and trehalose, resulting in a decrease in the reaction rate of the H(+)-ATPase from the plasma membrane of Kluyveromyces lactis. A direct correlation was found between viscosity (eta) and the inhibition of the maximum rate of catalysis (V(max)). The protocol used to measure viscosity by means of a falling ball type viscometer is described, together with the determination of enzyme kinetics and the application of Kramers' equation to evaluate the effect of viscosity on the rate of ATP hydrolysis by the H(+)-ATPase.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Trehalose-mediated inhibition of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase from Kluyveromyces lactis: dependence on viscosity and temperature.J Bacteriol. 2002 Aug;184(16):4384-91. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.16.4384-4391.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12142408 Free PMC article.
-
Tests of Kramers' Theory at the Single-Molecule Level: Evidence for Folding of an Isolated RNA Tertiary Interaction at the Viscous Speed Limit.J Phys Chem B. 2018 Sep 27;122(38):8796-8804. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b04014. Epub 2018 Sep 18. J Phys Chem B. 2018. PMID: 30078323
-
Trehalose-enzyme interactions result in structure stabilization and activity inhibition. The role of viscosity.Mol Cell Biochem. 2004 Jan-Feb;256-257(1-2):319-27. doi: 10.1023/b:mcbi.0000009878.21929.eb. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 14977191
-
Solvent viscosity and friction in protein folding dynamics.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2010 Aug;11(5):385-95. doi: 10.2174/138920310791330596. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2010. PMID: 20426733 Review.
-
Protein folding as a diffusional process.Biochemistry. 1999 Oct 19;38(42):13773-9. doi: 10.1021/bi991503o. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10529221 Review.
Cited by
-
Complete microviscosity maps of living plant cells and tissues with a toolbox of targeting mechanoprobes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jul 28;117(30):18110-18118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1921374117. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32669427 Free PMC article.
-
Immobilization of the Aspartate Ammonia-Lyase from Pseudomonas fluorescens R124 on Magnetic Nanoparticles: Characterization and Kinetics.Chembiochem. 2022 Apr 5;23(7):e202100708. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202100708. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Chembiochem. 2022. PMID: 35114050 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Eutectic Solvents as New Reaction Media to Produce Alkyl-Glycosides Using Alpha-Amylase from Thermotoga maritima.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 31;20(21):5439. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215439. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31683666 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of medium viscosity on kinetics of ATP hydrolysis by the chloroplast coupling factor CF1.Photosynth Res. 2016 May;128(2):163-8. doi: 10.1007/s11120-015-0213-y. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Photosynth Res. 2016. PMID: 26754050
-
The viscoelastic properties of Nicotiana tabacum BY-2 suspension cell lines adapted to high osmolarity.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Feb 25;25(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06232-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39994523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kramers HA. Brownian motion in a field of force and the diffusion model of chemical reactions. Physica. 1940;7:284–304.
-
- Jacob M, Geeves M, Holterman G, Schmid FX. Diffusional crossing in a two-state protein folding reaction. Nature Struc Biol. 1999;6:923–926. - PubMed
-
- Demchenko AP, Ruskyn OI, Saburova EA. Kinetics of the lactate dehydrogenase reaction in high-viscosity media. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989;998:196–203. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

