Outcomes of interferon alpha and ribavirin treatment for chronic hepatitis C in patients with normal serum aminotransaminases
- PMID: 14570736
- PMCID: PMC1773858
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.52.11.1644
Outcomes of interferon alpha and ribavirin treatment for chronic hepatitis C in patients with normal serum aminotransaminases
Abstract
Introduction: Information on treatment outcomes with interferon plus ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients with normal alanine aminotransaminase (ALT) levels is limited.
Aim: The aims of this study were to assess outcomes of treatment with interferon plus ribavirin in patients with normal ALT levels (normal ALT group, n=52) compared with those with elevated ALT levels (raised ALT group, n=53), and to document the rate at which patients with normal ALT levels have an apparent worsening of disease, as shown by increases in ALT levels.
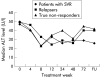
Results: At the end of treatment (week 48), 31 patients (59.6%) in the normal ALT group and 30 patients (56.6%) in the raised ALT group had undetectable hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA (p=0.75). A sustained virological response (SVR) was achieved in 20 patients (38.5%) in the normal ALT group and in 21 patients (39.6%) in the raised ALT group (p=0.90). Patients were subsequently followed up for a median of 29.8 (interquartile range 25th-75th percentile (IQR) 20.8-36.2) months in the normal ALT group and for a median of 26.1 (IQR 17.7-36.3) months in the raised group (p=0.20) after week 72 of treatment. Among patients without SVR in the normal ALT group, only three patients (9.4%) developed persistently raised ALT levels following therapy.
Conclusions: Combination therapy with interferon plus ribavirin is associated with a similar SVR in patients with normal ALT levels compared with those with elevated ALT levels. In patients with normal ALT levels, virological non-response to therapy results in new elevations in serum ALT levels in a small minority only.
Figures
Comment in
-
Hepatitis C infection with normal transaminases: is the treatment worse than the disease?Gastroenterology. 2004 Aug;127(2):677-9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.03.080. Gastroenterology. 2004. PMID: 15300601 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alter M, Kruszon-Moran D, Nainan OV, et al. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1988 through 1994. N Engl J Med 1999;341:556–62. - PubMed
-
- Di Bisceglie A, Goodman ZD, Ishak KG, et al. Long-term clinical and histopathological follow-up of chronic post-transfusion hepatitis. Hepatology 1991;14:969–74. - PubMed
-
- Seeff L, Buskell-Bales Z, Wright EC, et al. Long-term mortality after transfusion-associated non-A, non-B hepatitis. The National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Study Group. N Engl J Med 1992;327:1906–11. - PubMed
-
- Dienstag JL, Alter HJ. Non-A, non-B hepatitis: evolving epidemiologic and clinical perspective. Semin Liver Dis 1996;6:67–81. - PubMed
-
- Bacon BR. Treatment of patients with hepatitis C and normal serum aminotransferase levels. Hepatology 2002;36:S179–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources