The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: a missing link in neuroimmunomodulation
- PMID: 14571320
- PMCID: PMC1430829
The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: a missing link in neuroimmunomodulation
Abstract
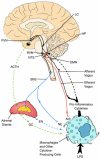
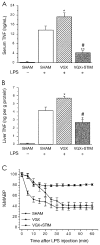
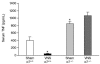
This review outlines the mechanisms underlying the interaction between the nervous and immune systems of the host in response to an immune challenge. The main focus is the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway, which we recently described as a novel function of the efferent vagus nerve. This pathway plays a critical role in controlling the inflammatory response through interaction with peripheral a7 subunit-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed on macrophages. We describe the modulation of systemic and local inflammation by the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway and its function as an interface between the brain and the immune system. The clinical implications of this novel mechanism also are discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Sell S. (2001) Immunology, immunopathology, and immunity (6th ed). ASM Press, Washington, D.C.
-
- Baumann H, Gauldie J. The acute phase response. Immunol Today. 1994;15:74–80. - PubMed
-
- Koj A. Initiation of acute phase response and synthesis of cytokines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1317:84–94. - PubMed
-
- Tracey KJ, et al. Shock and tissues injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986;234:470–4. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, et al. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science. 1999;285:248–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
