Role of cyclooxygenase enzymes in a murine model of experimental cholera
- PMID: 14573642
- PMCID: PMC219558
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.11.6234-6242.2003
Role of cyclooxygenase enzymes in a murine model of experimental cholera
Abstract
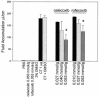
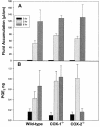
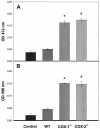
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., indomethacin) inhibit and reduce the fluid secretion responses elicited by cholera toxin (CT), but it has not been conclusively determined which cyclooxygenase (COX) isoform is involved in CT's action. This study evaluated the role of the COX enzymes and their arachidonic acid metabolites in experimental cholera. Swiss-Webster mice were dosed with celecoxib and rofecoxib and challenged with CT in ligated small intestinal loops, and intestinal segments from mice deficient in COX-1 and COX-2 were challenged with CT. The effects of CT on fluid accumulation, prostaglandin E(2) production, mucosal tissue injury, and markers of oxidative stress were measured. Celecoxib and rofecoxib given at 160 micro g per mouse inhibited CT-induced fluid accumulation by 48% and 31%, respectively, but there was no significant difference among cox-1(-/-) and cox-2(-/-) mice in response to CT compared to wild-type controls. CT elevated tissue levels of oxidized glutathione and lipid peroxides and elicited small intestinal tissue injury in two of five cox-1(-/-) and four of five cox-2(-/-) mice. A role for COX-2 in CT's mechanism of action has previously been suggested by the effectiveness of COX-2 inhibitors in reducing CT-induced fluid secretion, but CT challenge of COX-1 and COX-2 knockout mice did not corroborate the pharmacological data. The results of this study show that CT induced oxidative stress in COX-deficient mice and suggest a tissue-protective role for arachidonic acid metabolites in the small intestine against oxidative stress.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cholera toxin induces prostaglandin synthesis via post-transcriptional activation of cyclooxygenase-2 in the rat jejunum.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Jun;297(3):940-5. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001. PMID: 11356914
-
Rofecoxib [Vioxx, MK-0966; 4-(4'-methylsulfonylphenyl)-3-phenyl-2-(5H)-furanone]: a potent and orally active cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. Pharmacological and biochemical profiles.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Aug;290(2):551-60. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999. PMID: 10411562
-
Effect of the selective COX-2 inhibitors, celecoxib and rofecoxib in rat acute models of inflammation.Inflamm Res. 2002 Dec;51(12):603-10. doi: 10.1007/pl00012435. Inflamm Res. 2002. PMID: 12558194
-
The new NSAIDs: cox-2 inhibitors.Medsurg Nurs. 2000 Dec;9(6):313-7. Medsurg Nurs. 2000. PMID: 11904867 Review. No abstract available.
-
[Specific inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2): current knowledge and perspectives].Acta Biomed Ateneo Parmense. 2001;72(3-4):55-64. Acta Biomed Ateneo Parmense. 2001. PMID: 11889908 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Toxin mediated diarrhea in the 21 century: the pathophysiology of intestinal ion transport in the course of ETEC, V. cholerae and rotavirus infection.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Aug;2(8):2132-57. doi: 10.3390/toxins2082132. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin-like growth factor I improves intestinal barrier function in cirrhotic rats.Gut. 2006 Sep;55(9):1306-12. doi: 10.1136/gut.2005.079988. Epub 2006 Jan 24. Gut. 2006. PMID: 16434425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold, J. W., D. W. Niesel, C. R. Annable, C. B. Hess, M. Asuncion, Y. J. Cho, J. W. Peterson, and G. R. Klimpel. 1993. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates the early pathology in Salmonella infection of the gastrointestinal tract. Microb. Pathog. 14:217-227. - PubMed
-
- Bennett, A. 1971. Cholera and prostaglandins. Nature 231:536. - PubMed
-
- Beubler, E., and G. Horina. 1990. 5-Hydroxytryptamine2 and 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptor subtypes mediate cholera toxin-induced intestinal fluid secretion in the rat. Gastroenterology 99:83-89. - PubMed
-
- Beubler, E., G. Kollar, A. Saria, K. Bukhave, and J. Rask-Madsen. 1989. Involvement of 5-hydroxytryptamine, prostaglandin E2, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate in cholera toxin-induced fluid secretion in the small intestine of the rat in vivo. Gastroenterology 96:368-376. - PubMed
-
- Beubler, E., R. Schuligoi, A. K. Chopra, D. A. Ribardo, and B. A. Peskar. 2001. CT induces prostaglandin synthesis via post-transcriptional activation of cyclooxygenase-2 in the rat jejunum. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 297:940-945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

