Low-level pilin expression allows for substantial DNA transformation competence in Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- PMID: 14573647
- PMCID: PMC219589
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.11.6279-6291.2003
Low-level pilin expression allows for substantial DNA transformation competence in Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Abstract
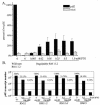
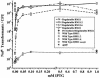
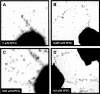
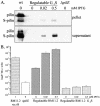
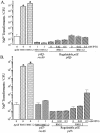
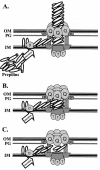
The gonococcal pilus is a major virulence factor that has well-established roles in mediating epithelial cell adherence and DNA transformation. Gonococci expressing four gonococcal pilin variants with distinct piliation properties under control of the lac regulatory system were grown in different levels of the inducer isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG). These pilin variants expressed various levels of pilin message and pilin protein in response to the level of IPTG in the growth medium. Moreover, posttranslational modifications of the variant pilin proteins were detected, including S-pilin production and glycosylation. The ratio of the modified and unmodified pilin forms did not substantially change with different levels of pilin expression, showing that these modifications are not linked to pilin expression levels. DNA transformation competence was also influenced by IPTG levels in the growth medium. Substantial increases in transformation competence over an isogenic, nonpiliated mutant were observed when limited amounts of three of the pilin variants were expressed. Immunoelectron microscopy showed that when limited amounts of pilin are expressed, pili are rare and do not explain the pilin-dependent transformation competence. This pilin-dependent transformation competence required prepilin processing, the outer membrane secretin PilQ, and the twitching-motility-regulating protein PilT. These requirements show that a fully functional pilus assembly apparatus is required for DNA uptake when limited pilin is produced. We conclude that the pilus assembly apparatus functions to import DNA into the bacterial cell in a pilin-dependent manner but that extended pili are not required for transformation competence.
Figures


References
-
- Aas, F. E., C. Lovold, and M. Koomey. 2002. An inhibitor of DNA binding and uptake events dictates the proficiency of genetic transformation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: mechanism of action and links to type IV pilus expression. Mol. Microbiol. 46:1441-1450. - PubMed
-
- Bradley, D. E. 1980. A function of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO polar pili: twitching motility. Can. J. Microbiol. 26:146-154. - PubMed
-
- Chen, I., and D. Dubnau. 2003. DNA transport during transformation. Front Biosci. 8:S544-S556. - PubMed
-
- Drake, S. L., and M. Koomey. 1995. The product of the pilQ gene is essential for the biogenesis of type IV pili in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol. Microbiol. 18:975-986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI33493/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI044239/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI07476/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI31494/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AI010568/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI44239/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007476/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008061/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM08061/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI031494/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI033493/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033493/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AI10568/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

